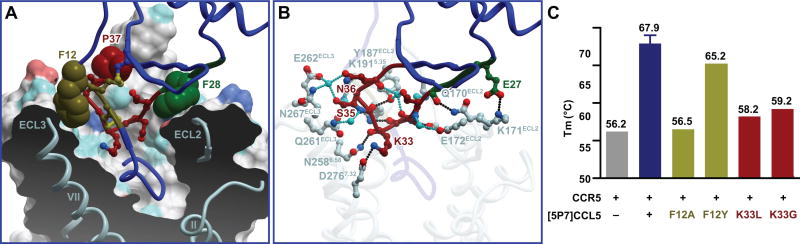
Figure 5. N-loop and 30s loop interactions represent new motifs in receptor-chemokine interactions.
(A) Steric interactions of the N-loop (brown), 30s loop (red), and β1-strand (green) of [5P7]CCL5 (blue ribbon except for the highlighted parts) with the TM domain and ECLs of CCR5. Residues involved in aromatic stacking interactions are shown as spheres. The receptor is shown as a cut-away surface colored as in Figure 3.
(B) Polar interactions of [5P7]CCL5 30s loop (red), and β1-strand (green) with the CCR5 binding pocket and ECLs. Direct and water-mediated receptor-chemokine hydrogen bonds are shown in black and cyan, respectively.
(C) The effect of mutations of [5P7]CCL5 residues K33 and F12 on the thermostability of CCR5-[5P7]CCL5 complexes.
See also Table S2 and Table S3.