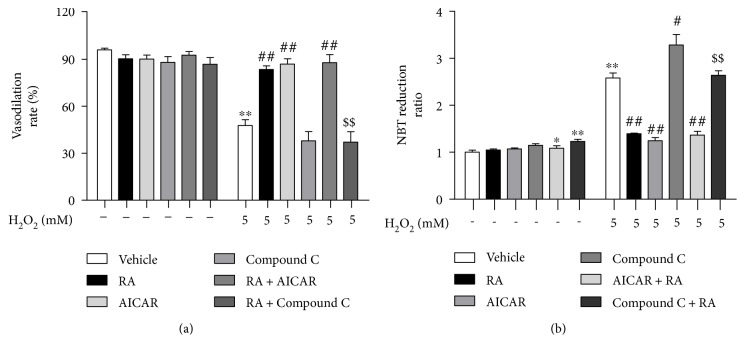
Figure 4.
AMPK activation mediated the protection of rosmarinic acid against the endothelial dysfunction induced by H2O2 in rat aortic rings. The rat aortic rings were cotreated with AMPK activator AICAR (50 μM, 10 min) or inhibitor compound C (10 μM) and RA (50 μM) for 10 min, then exposed to H2O2 (5.0 mM) for another 10 min. The endothelial function was assessed by the endothelium-dependent vasodilation induced by acetylcholine (ACh, 10 μM). (a) The relative endothelium-dependent vasodilative rate after exposure to RA, AMPK modulator, and H2O2 in rat aortic rings. (b) The NBT reduction after exposure to RA, AMPK modulator, and H2O2 in rat aortic rings. Data are presented as the means ± SD (n = 6). ∗P < 0.05 versus the untreated control group; ∗∗P < 0.01 versus the untreated control group; ##P < 0.01 versus the H2O2-treated group; $$P < 0.01 versus the H2O2- and RA-cotreated groups.