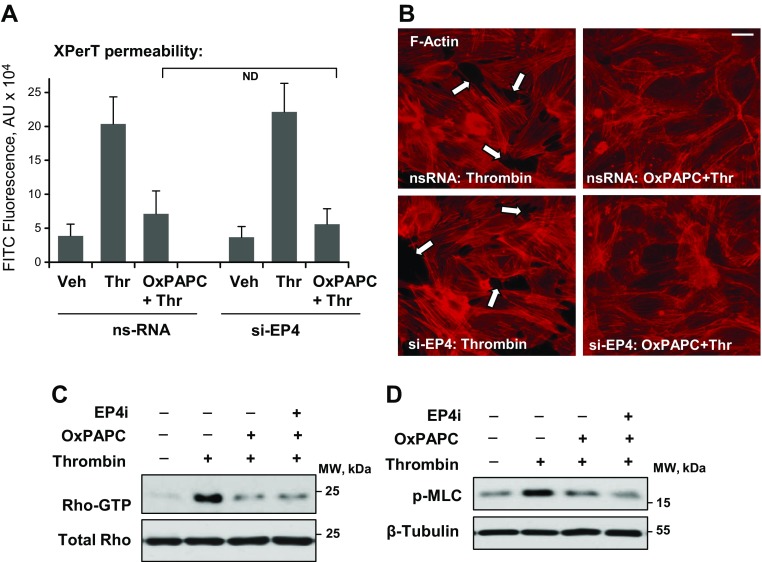
Figure 4.
EP4 is not involved in the OxPAPC protective effects against thrombin-induced EC permeability. Pulmonary EC monolayers that were pretreated with control or EP4-specific siRNA were pretreated with OxPAPC (15 µg/ml, 30 min) or vehicle followed by thrombin (0.5 U/ml) stimulation. A) Analysis of EC permeability for macromolecules by using FITC-labeled avidin tracer. Accumulation of FITC-avidin on the substrate that underlies EC monolayers reflecting EC barrier dysfunction was assessed by fluorimetric analysis as described in Materials and Methods (n = 6). B) Effect of EP4 knockdown on the OxPAPC-induced attenuation of thrombin-induced formation of actin stress fibers and paracellular gaps. F-actin was visualized by cell staining with Texas Red phalloidin. Paracellular gaps are marked by arrows. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments. Scale bar, 10 µm. C, D) Thrombin-induced activation of RhoA GTPase measured in pulldown assays (C) and Rho kinase–mediated phosphorylation of myosin light chains (MLCs) (D) detected by Western blot was evaluated in ECs after thrombin challenge with or without OxPAPC or EP4 inhibitor L161982 (3 µM, 1 h) pretreatment. Membrane probing with Ab to β-tubulin was used as a normalization control. ND, no difference; ns, nonspecific; thr, thrombin; veh, vehicle.