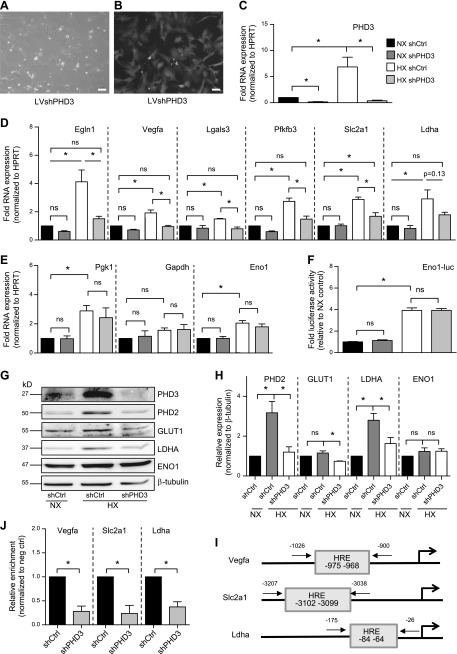
Figure 3.
PHD3 controls expression of a select set of HIF-1 targets in NP cells through a p300-dependent mechanism. A, B) Bright-field (A) and fluorescent (B) images of rat NP cells after transduction with lentivirus coexpressing shPHD3 and enhanced green fluorescent protein. Scale bars, 10 μm. C) Measurement of PHD3 mRNA expression after transduction of NP cells with shRNA targeting PHD3 (n = 7). D) Measurement of mRNA expression of HIF-1 target genes in PHD3-silenced NP cells cultured in NX or HX for 72 h (n = 7). E) Hypoxic expression of Pgk1, Gapdh, and Eno1 in PHD3-silenced cells did not change (n = 3). F) Measurement of activity of Eno1 promoter containing 2 well-characterized HIF-1 binding sites after PHD3 knockdown (n = 7). G, H) Western blot (G) and corresponding densitometric analysis (H) of select HIF-1 targets in NP cells after stable knockdown of PHD3 (n = 4). I) Location of HRE sites within promoters of Vegfa, Slc2a1, and Ldha and location of ChIP primers used in J. J) HIF-1α enrichment at HRE sites within Vegfa, Slc2a1, and Ldha promoters decreases after knockdown of PHD3 during 72 h HX (n = 3). Luciferase assays were performed with 3 technical replicates per experiment; quantitative RT-PCR assays were performed with 2 technical replicates per experiment. Data are means ± sem. *P < 0.05.