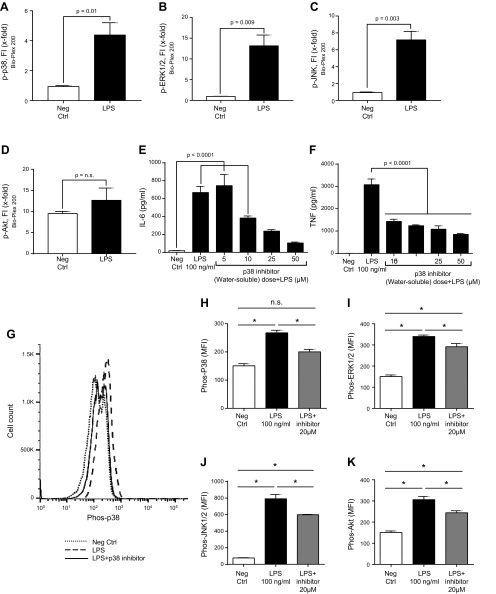
Figure 4.
Phosphorylation of mouse PEMs (1 h at 37°C) caused by LPS (100 ng/ml). A–D) Bio-Plex phosphoprotein assay analysis of intracellular phospho-MAPKs p-p38 (A), p-ERK1/2 (B), and p-JNK (C) or p-AKT (D). Neg Ctrl, negative control. E, F) Dose response test of water-soluble p38 inhibitor (5–50 µM), in which the IC50 was used, indicated a dose-related reduction in release of IL-6 (E) and TNF (F). G–K) In vitro reductions in phospho-MAPKs and Akt in PEMs exposed to LPS in the absence or presence of 20 µM water-soluble inhibitor of p38. G) Typical example of PEMs exposed to buffer (neg ctrl) or to LPS in the presence or absence of the p38 inhibitor, using flow cytometry as the end point for phospho-Akt or phospho-MAPKs, as described in Fig. 1. H–K) Levels of mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) indicating the levels of phospho-MAPKs p-p38 (H), p-ERK1/2 (I), and p-JNK (J) or p-AKT (K) in PEMs exposed to LPS in the absence or presence of 20 µM water-soluble inhibitor of p38. Data are expressed as means ± sem (n ≥ 5 samples per group). *P < 0.05.