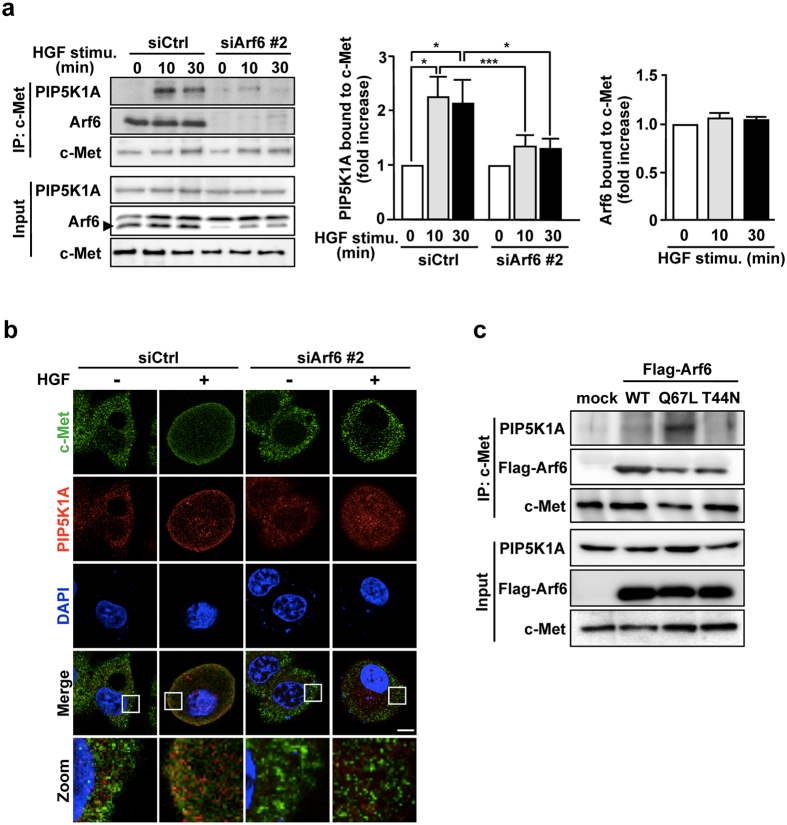
Figure 3.
Arf6 activated by HGF stimulation forms a complex with PIP5K1A and c-Met. (a) After HepG2 cells transfected with siRNAs for control and Arf6 were stimulated with 10 ng/mL of HGF for the indicated time, c-Met was immunoprecipitated with anti-c-Met antibody, and co-precipitated Arf6 and PIP5K1A were assessed by Western blotting with anti-Arf6 and anti-PIP5K1A antibodies, respectively (left panels). Signal intensities of co-precipitated PIP5K1A (middle panel) and Arf6 (right panel) were quantified. Shown are means ± SEM from three independent experiments. Statistical analyses: two-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni’s test (for PIP5K1A bound to c-Met) and one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s test (for Arf6 bound to c-Met). *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001. (b) HepG2 cells transfected with siRNAs for control and Arf6 were stimulated with HGF as in Fig. 1a, and immunostained for c-Met and PIP5K1A. Nuclei were also stained with DAPI. Area of squares in images were magnified and shown in the bottom. Scale bar, 10 μm. Green, c-Met; Red, PIP5K1A; Blue, DAPI. (c) HepG2 cells were transfected with a control plasmid and plasmids for Flag-tagged Arf6 mutants, Q67L and T44N. After c-Met was immunoprecipitated, co-precipitated PIP5K1A and Flag-Arf6 mutants were assessed by Western blotting with anti-PIP5K1A and -Flag antibodies, respectively. Blots shown in (a and c) are cropped images. The full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure.