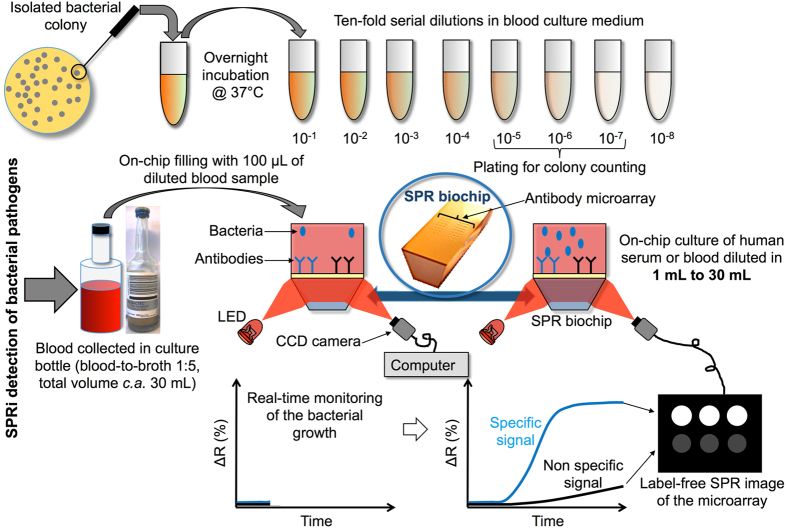
Figure 1.
Label-free detection of bacteria in blood using protein microarrays and SPRi detection. Bacteria from an isolated bacterial colony were grown overnight in blood culture medium. Then, the culture was ten-fold serially diluted in the same medium and a diluted aliquot was finally mixed with blood samples so that the blood-to-broth ratio was kept constant (1:5) similarly to conditions routinely used in clinical settings. Several dozens of antibodies can be arrayed on 1 cm2. Live bacteria are captured on microarrayed specific antibodies (spotted in triplicate onto the biochip surface) during the enrichment step. SPRi data are treated and plotted as variations of light reflectivity (ΔR (%)) over time for each region-of-interest (corresponding to antibody spots arrayed on the sensor). Differential SPR images (obtained by subtracting a reference SPR image recorded at t(0) to any SPR image acquired later in the experiment) may also be displayed.