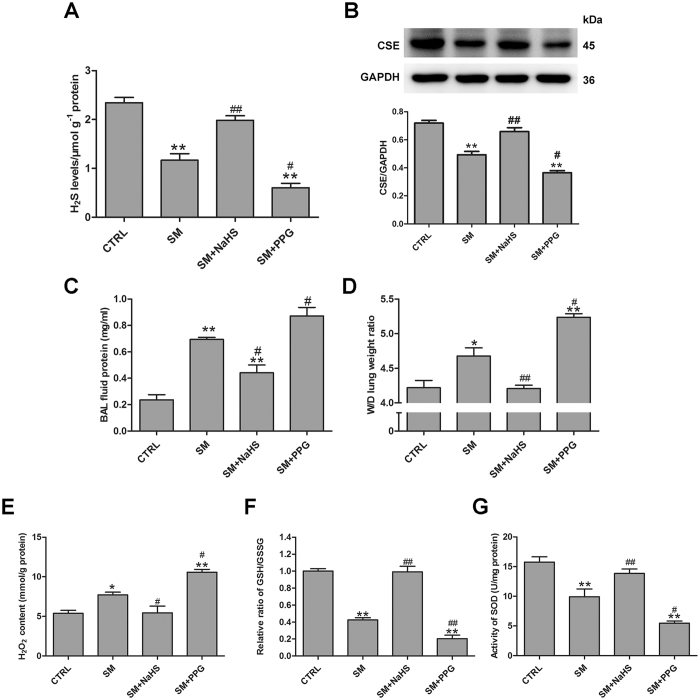
Figure 2.
Inhibition of H2S reduction protects against SM-induced lung injury. Mice were subcutaneously injected with SM (30 mg/kg), with or without intraperitoneal administration of NaHS (5 mg/kg) or intraperitoneal administration of PPG (30 mg/kg), addition NaHS and PPG were given every day for a total of three doses. Sulfide concentrations (A) and CSE protein expression (B) were determined by RHP-2 and western blot, respectively. Measurement of protein concentration was performed in BAL fluid (C). Lung W/D (D) was measured as an index of pulmonary edema formation. H2O2 content (E), GHS/GSSG ratio (F), SOD activity (G) in mouse lungs were measured as oxidative stress parameters. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM(n = 5). *p < 0.05 vs CTRL group; **p < 0.01 vs CTRL group; #p < 0.05 vs SM group; ##p < 0.01 vs SM group.