Fig. 1.
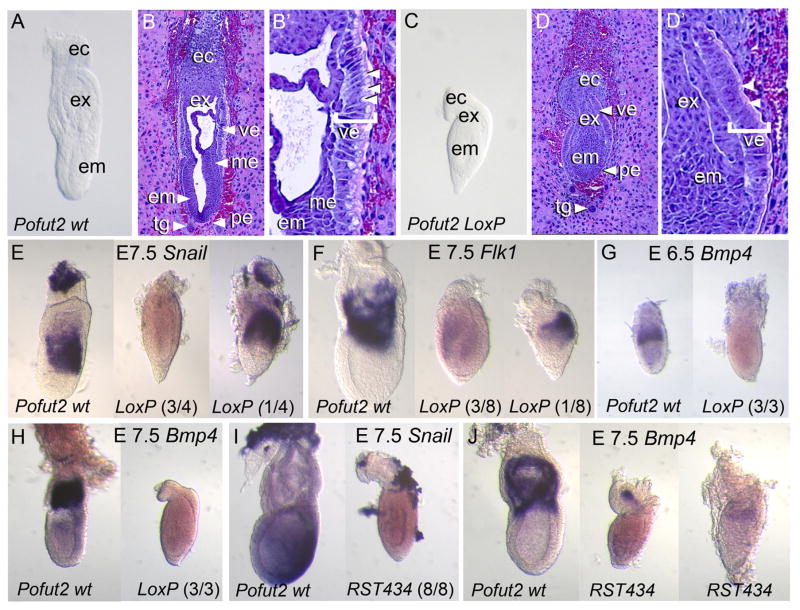
POFUT2 is essential for maintaining epithelial organization and mesoderm differentiation. (A–D′) Comparison of E 7.5 Pofut2 wild-type (Pofut2 wt) and Pofut2 knockout embryos (Pofut2-LoxP) by gross morphology (A and C) and hematoxylin and eosin staining of sections (B and D). Embryo orientation: proximal up and distal down; anterior left and posterior right. (A–B′) wild-type embryos have well-defined embryonic (embryonic ectoderm, ec; mesoderm, me) and extraembryonic tissues (ectoplacental cone, ec; extraembryonic ectoderm, ex; embryonic ectoderm, em; visceral endoderm, ve; parietal endoderm, pe; trophoblast giant cells, tg). (B′) The proximal visceral endoderm (bracketed) is highly polarized and has large apical vacuoles (arrowheads). (C–D′) In contrast, tissues in Pofut2 knockout embryos are highly compressed, mesoderm is not clearly visible, and extraembryonic structures derived from mesoderm are absent. (D′) The Pofut2 knockout visceral endoderm, although polarized, lacks large apical vacuoles (arrowheads). (E–J) Comparison of mesodermal (Snail and Flk1) and mesodermal and extraembryonic ectoderm (Bmp4) marker expression using whole mount in situ hybridization. Where the expression patterns varied in Pofut2 mutants, representative embryos are shown with number of embryos in indicated in parenthesis. (E–F) Comparison of gene expression in wild-type (left) and Pofut2-LoxP mutants (right). In contrast to E 7.5 wild-type embryos, the majority of Pofut2 mutants fail to express these genes, or expressed them at lower levels. Note that 4/8 Pofut2-LoxP mutants did not express Flk1 (not shown). (I, J) Comparison of Snail (I) and Bmp4 (J) expression in wild-type (left) and Pofut2-RST434 mutant littermates (right). Pofut2-RST434 mutants lack Snail mRNA and show only limited expression of Bmp4 in the extraembryonic region. In this study, the Pofut2-RST434 had been back-crossed more than 20 generations to C57BL/6J. Embryos are oriented proximal up and distal down. Wild-type embryos are oriented anterior to the left; Anterior posterior orientation of Pofut2 mutants is not known.