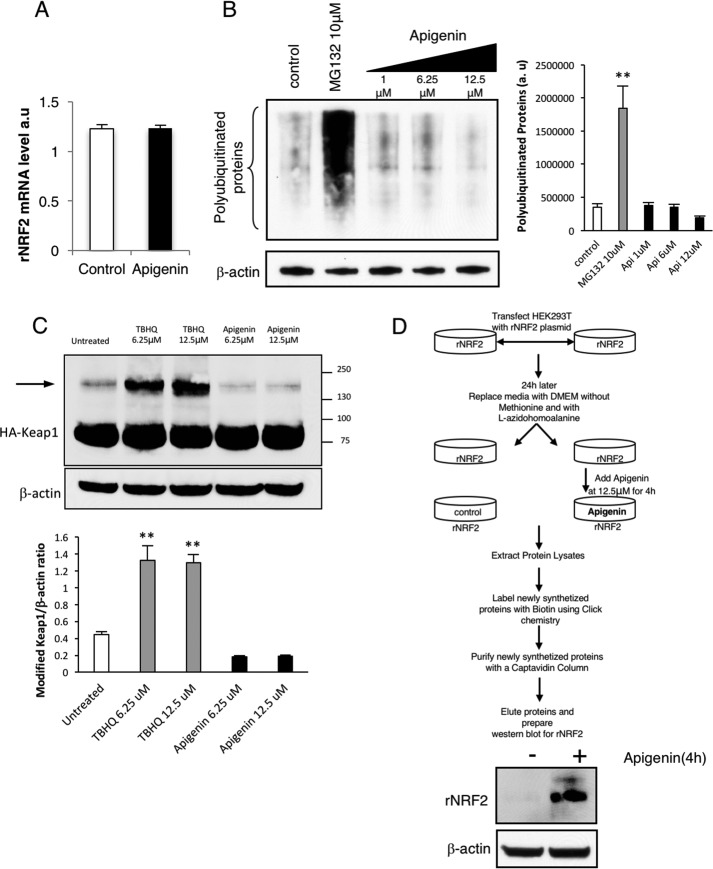
Figure 6.
Apigenin activates the translation of Nrf2. A, real-time PCR indicated that apigenin did not affect the transcription of rNrf2 in HEK293T cells. B, analysis of polyubiquitinated proteins in HEK293T cells after apigenin treatment suggested that it was not an inhibitor of the proteasome (n = 3). As a positive control, the effect of the proteasome inhibitor MG132 was included in the assay. The relative intensity of the signal from the polyubiquitinated proteins is indicated as a ratio with β-actin as the loading control. The statistical significance of the difference in the levels of polyubiquitinated proteins in treated versus control cells is indicated by **, p < 0.01. C, apigenin treatment of HA-Keap1-transfected HEK293T cells did not induce post-translational modifications in Keap1 (arrow) when compared with TBHQ, a well-known inhibitor of the Nrf2 degradation mediated by Keap1 (n = 3). The relative intensity of the bands for modified Keap1 is indicated as a ratio with β-actin as a loading control. The statistical significance of the difference in the levels of modified Keap1 in treated versus untreated cells is indicated by **, p < 0.01. The arrow indicates the appearance of a slow migrating isoform of Keap1 due to cysteine disulfur bridge formation. D, apigenin activated the translation of Nrf2. An assay to isolate newly synthesized proteins was performed by following the steps indicated in the top diagram. The presence of newly synthesized recombinant Nrf2 in the eluates from cells treated or untreated with apigenin was evaluated by Western blotting (n = 3).