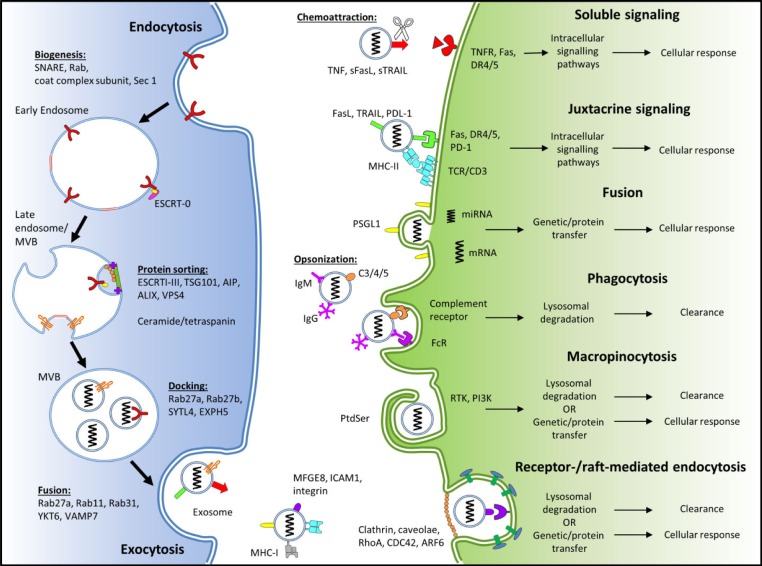
Figure 1.
Schematic of exosome biogenesis, internalization and cellular response. The adhesion of exosomes to the recipient cell utilizes the interaction of various exosomal surface proteins and cellular receptors. Once bound, the exosome may (i) elicit transduction of the signal via intracellular signalling pathways and be released (juxtacrine signalling); (ii) fuse with the cellular membrane transferring protein and genetic contents, into the cytoplasm of the recipient cell (fusion); or (iii) be endocytosed via phagocytosis, macropinocytosis or receptor-mediated endocytosis. This figure was produced using Servier Medical Art, available from www.servier.com/Powerpoint-image-bank.