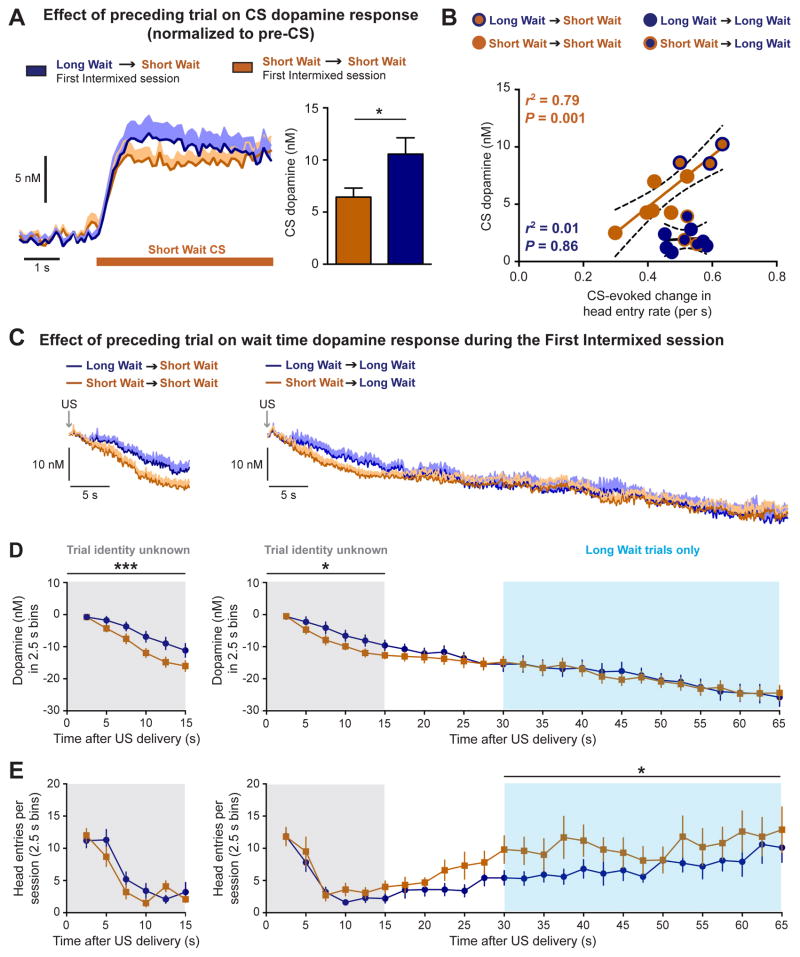
Figure 5.
The preceding trial influences CS-evoked dopamine release and wait time dopamine levels in opposing directions. (A) The identity of the preceding trial influenced the dopamine response to the Short Wait CS during the First Intermixed training session (* p < 0.05, paired t-test). (B) Conditioned responding is related to a CS-specific change in dopamine release. (C) Average dopamine response during the current Short Wait trial (left) and the current Long Wait trial (right) as a function of the identity of the preceding trial. (D) Wait time dopamine response in 2.5 s bins. Grey overlay denotes temporal window where the identity of the current trial is unknown. Blue overlay denotes temporal window experienced only during Long Wait trials. The previous trial influences the magnitude of the wait dopamine response when the identity of the current trial is unknown (*, *** p < 0.05, p < 0.001; effect of previous trial). (E) Head entries during the wait time in 2.5 s bins. The previous trial influences the number of head entries during the period of time only experienced during Long Wait trials. (* p < 0.05, effect of previous trial). Data are represented as mean ± SEM.