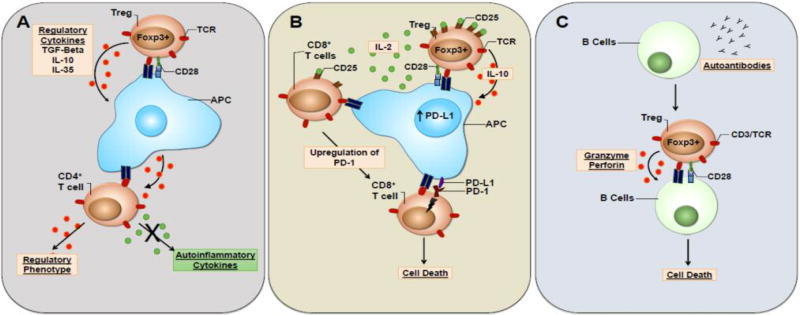
Figure 1.
Treg cell mechanism of suppression in autoimmunity. (A) When activated, Treg cells are capable of driving the formation of tolerogenic APCs via the secretion of regulatory cytokines (e.g., TGF-β and IL-10). Tolerogenic APCs activate antigen-specific CD4+ T cells and skew them towards a regulatory phenotype. (B) IL-2 cytokine depletion drives the upregulation of PD-1 on activated CD8+ T cells. Upregulation of PD-L1 by tolerogenic APCs, leave CD8 T cells vulnerable to cell death in a PD-1/PDL-1 dependent manner. (C) B cells are capable of presenting antigens to Treg cells. Once activated by B cells, Tregs suppress the secretion of autoantibodies via direct killing of autoinflammatory B cells in a perforin and granzyme dependent manner.