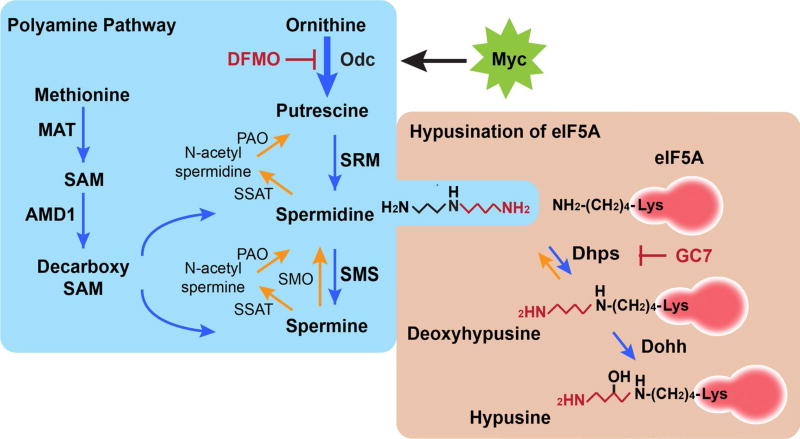
Fig. 1.
The polyamine-hypusine pathway. The most common polyamines are putrescine, spermidine and spermine, which are predominantly derived from the amino acids ornithine and methionine. One of the polyamines, spermidine, is used as the substrate to synthesize a unique amino acid coined hypusine, which is covalently linked to the lysine-50 residue of eIF5A. In cancer cells, ornithine decarboxylase 1 (ODC1), the enzyme catalyzing the first step of polyamine biosynthesis, is often up-regulated, especially in Myc-driven malignant cancers, which in turn, increases levels of polyamines. As a result, the levels of polyamines are elevated in cancer cells. 2-difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) is suicide inhibitor of ODC1 and has shown impressive efficacy in several clinical cancer prevention trials, including colon and prostate cancer. Hypusination of eIF5A is mediated by two enzymes, DHPS and DOHH. Hypusination is conserved among all eukaryotes. MAT methionine adenosyltransferase, SAM S-adenosyl-l-methionine, AMD1 AdoMet decarboxylase, SRM spermidine synthase, SMS spermine synthase, SMO spermine oxidase, SSAT spermidine/ spermine N1-acetyltransferase, PAO polyamine oxidase