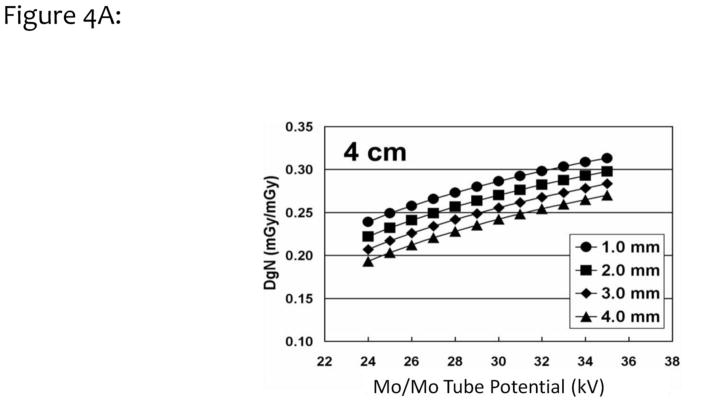
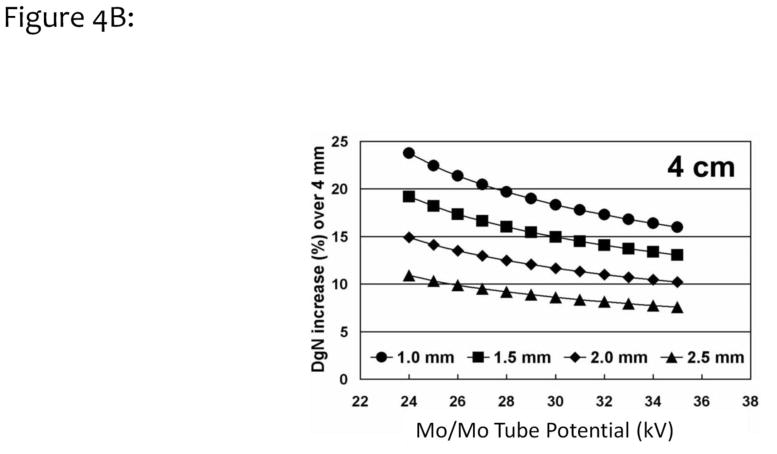
Figure 4.
Figure 4A. Monte Carlo studies were performed over a range of different skin thicknesses (from 1.0 to 4.0 mm, see legend), and the normalized glandular dose coefficients (DgN) were computed for a 4 cm compressed breast thickness. The DgN coefficients were evaluated at x-ray tube potentials ranging from 24 to 35 kV.
Adapted from a figure in reference 26
Figure 4B. Data similar to those shown in Fig. 4A were used for computing the increase in DgN coefficients, relative to a 4 mm skin thickness, for skin thicknesses ranging from 1.0 to 2.5 mm. For the typical tube potential use for imaging of a 4 cm thick breast (~28 kV), a 17% increase in the DgN coefficient was observed for the 1.5 –mm-thick skin.
Adapted from a figure in reference 26.