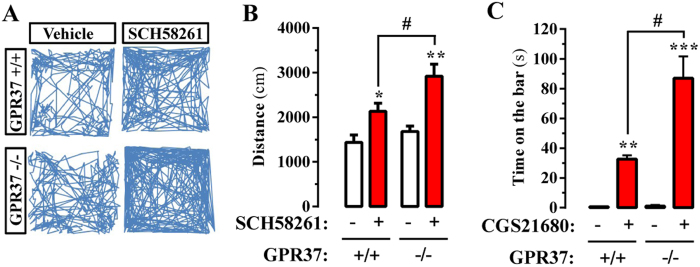
Figure 6.
GPR37 deletion promotes A2AR-mediated behavior. (A) A2AR antagonist-induced locomotor hyperactivity in GPR37+/+ and GPR37−/− mice. Representative 10 min trajectories in an open field arena of GPR37+/+ and GPR37−/− mice administered intraperitoneally with vehicle or SCH58261 (3.75 mg/kg). (B) Quantification of the horizontal locomotor activity shown in (A). The distance travelled is expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 10 animals) *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 SCH58261 treatment effect (one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post-hoc test), # P < 0.05 phenotype effect (two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post-hoc test). (C) A2AR agonist-induced catalepsy in GPR37+/+ and GPR37−/− mice. The cataleptic response induced by intracerebroventricular administration of CGS21680 (10 µl of a 1 µg/µl solution) in GPR37+/+ and GPR37−/− mice was measured as the duration of an abnormal upright posture in which the forepaws of the mouse were placed on a horizontal wooden bar. The time spent with both front paws resting on the bar is expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 10 animals); a cut off time was set at 200 s. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 CGS21680 treatment effect (one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post-hoc test); # P < 0.05 phenotype effect (Two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post-hoc test).