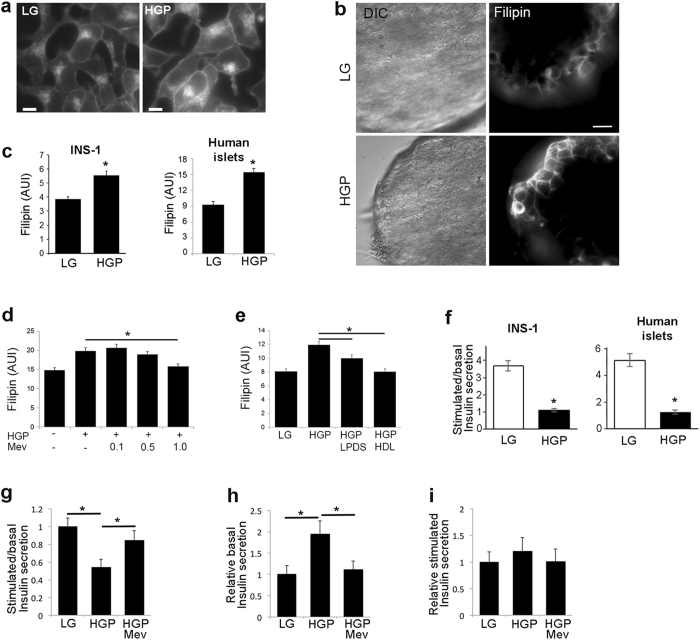
Figure 1.
Glucolipotoxicity increases free cholesterol and decreases insulin secretion. ( a–c) HGP increases free cholesterol. INS-1 cells (a) or human islets (b) were treated for 72 h with control growth medium (LG), or HGP. Filipin per cell, indicating free cholesterol, was quantified from 5 independent experiments (c). DIC, differential interference contrast. AUI, arbitrary unit of intensity. Scale bars, 10 μm. (d) Mevinolin (Mev), an inhibitor of cholesterol synthesis, blocks HGP-induced increase in filipin staining in a dose-dependent manner. Cells were treated with HGP and Mev (μM) in LPDS growth medium for 72 h. (e) LPDS or HDL treatment blocks HGP-induced increase in filipin staining. Cells were treated with LG, HGP, HGP in LPDS medium (HGP + LPDS) or HGP and HDL in LPDS medium (HGP + HDL) for 72 h. (f) HGP decreases GSIS. Static GSIS assays of INS-1 and human islets were performed in cells treated for 72 h with HGP. (g–i) Mev treatment normalizes GSIS (g) by inhibiting HGP-induced basal insulin secretion (h) without affecting stimulated insulin secretion (i). All values are expressed as fold change relative to LG. n = 5 experiments. *p < 0.05.