Figure 4.
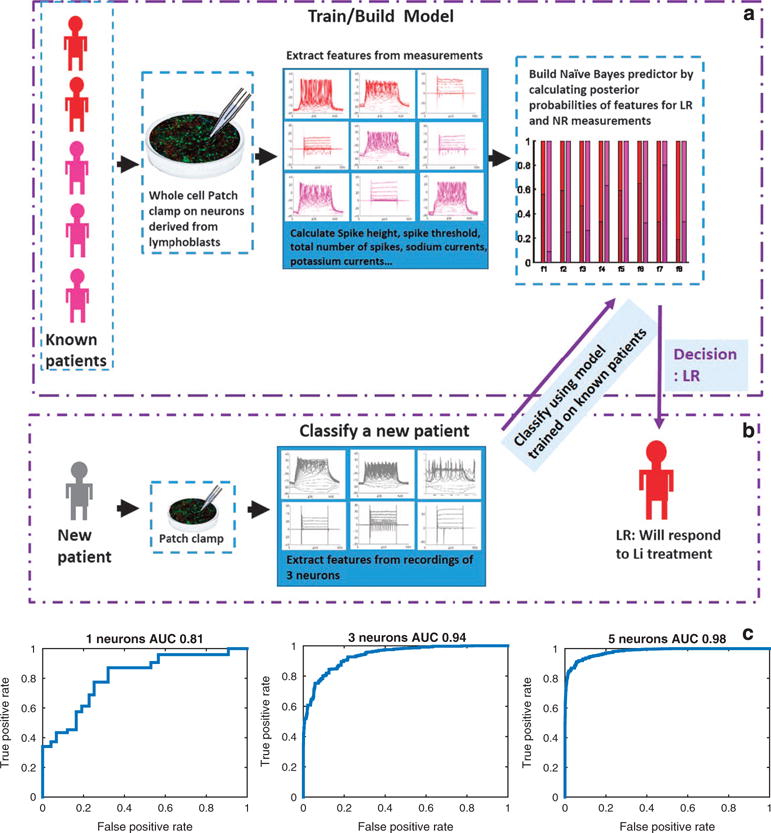
Classification of a patient as responsive or non-responsive to lithium (Li) based on electrophysiological measurements. (a) Building the model: The model is trained on five of the six patients. Features such as spike height and spike threshold (see Materials and Methods for the entire list) are extracted from patch-clamp measurements and a Naïve Bayes (NB) model is built using posterior probabilities of the features that are calculated from the data set of the five patients. The model shown in the graph shows the posterior probabilities of each of the features when the patients are lithium (Li)-responsive (LR) patients (shades of red) and Li-non-responsive (NR) patients (shades of purple). (b) To classify a new patient, we use patch-clamp recordings from three cells. The NB model that was trained on measurements of the other patients is used to give a posterior score of the new patient as being NR or LR given the features extracted from its three-cell recordings. The decision is made based on the maximum posterior probability. (c) Performance is assessed pulling together classification of the six patients (each with a model trained on the other five patients) using a receiver-operating characteristics (ROC) curve and the area under the curve (AUC). An ROC curve is shown for performance using one-cell recordings for classification, three-cell recordings or five-cell recordings. With five-cell recordings, the AUC is 0.98.
