FIG 1 .
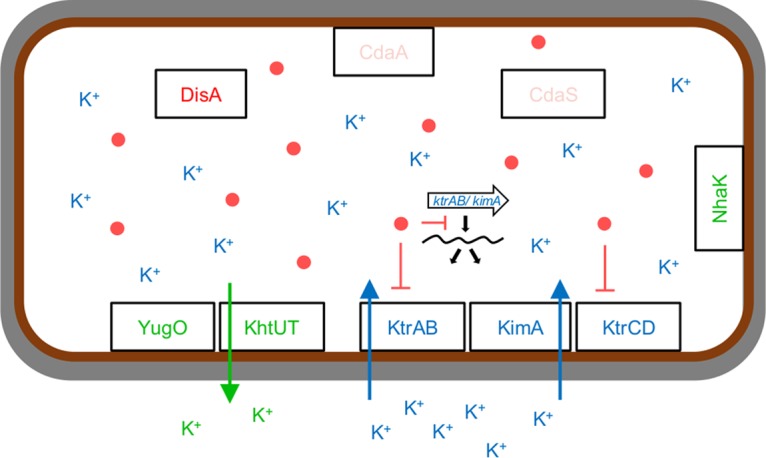
Cyclic di-AMP controls K+ uptake. When the external K+ concentration is low, c-di-AMP synthesis is reduced. The high-affinity K+ transporters ktrAB and kimA are expressed and c-di-AMP is transported into the cell. When the external K+ concentrations are high, c-di-AMP synthesis is increased. The second messenger binds to the ktrAB and kimA riboswitch (indicated by the large white arrow), preventing transcription of the respective genes encoding the high-affinity transporters. In addition, c-di-AMP negatively controls the activity of KtrAB and KtrCD by binding to the regulatory components KtrA and KtrC, respectively. YugO and KhtUT are K+ exporters, and NhaK is a monovalent cation/H+ antiporter (10). Red dots, c-di-AMP molecules.
