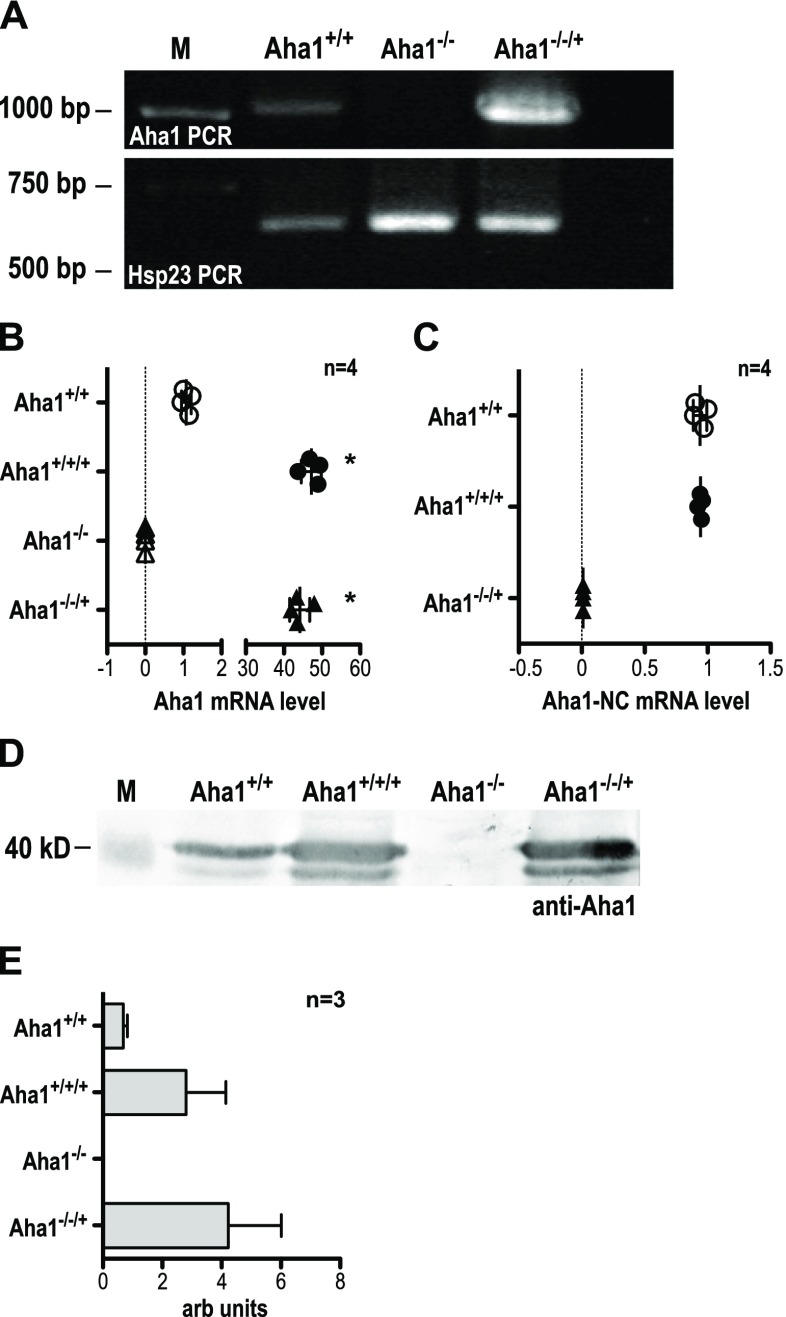
Fig. 4.
Verification of L. donovani Aha1−/− null mutants and control strains. a The gDNAs from L. donovani strains Aha1+/+ (wild type), Aha1−/− and Aha1−/−/+ were used as templates for an Aha1 gene-specific PCR (upper panel). The same gDNAs were also used as templates for amplification of Hsp23-coding DNA (bottom panel) to ascertain the quality of the gDNAs. b Aha1 mRNA levels (arbitrary units) were quantified by RT-qPCR for Aha1+/+, Aha1+/+/+, Aha1−/− and Aha1−/−/+ using primers against the coding region; n = 4; *p ≤ 0.05 (Mann-Whitney U test). c Another RT-qPCR from the same samples was performed targeting either side of the border between Aha1 CDS and 3′ NC; n = 4. d Lysates from L. donovani strains Aha1+/+, Aha1−/− and Aha1−/−/+ were separated by SDS-PAGE, subjected to Western blot and probed with chicken anti-Aha1. A replica gel was stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue as loading control (not shown). The position of the 40-kD-size marker is shown on the left; n = 3. e. Aha1 protein abundance (arbitrary units) was quantified by Western blot and densitometric analysis