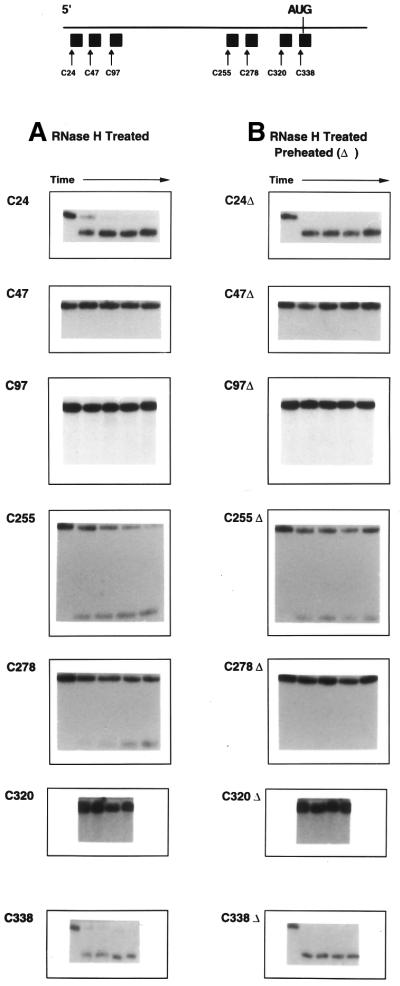
Figure 2.
RNase H treatment of HCV IRES RNA following hybridization with 20 base DNA oligonucleotides. The 32P-labeled 402 base transcript spanning the HCV IRES (Fig. 1) was prepared as described in Materials and Methods and treated with RNase H in the presence of various DNA oligonucleotides complementary to different regions of the IRES sequence as shown on the map at the top of the figure: C24, bases 24–43; C47, bases 47–66; C97, bases 97–116; C255, bases 255–274; C278, bases 278–297; C320, bases 320–339; C338, bases 338–360. In control reactions in the absence of DNA no RNase H cleavage occurs; similarly, in the presence of each DNA but without RNase H no cleavage is observed. (A) In the left column the results of mixing RNA substrate, a 1.5–2-fold molar excess of DNA and RNase H and incubating as described in Materials and Methods are shown. In each individual reaction profile the left-most lane represents time 0, while each lane to the right represents sequentially 5, 15, 30 and 60 min incubation. (B) The right column represents reactions in which substrate and DNA were preheated separately to 90°C, buffer added, the reactions mixed, cooled and RNase H added, as described in Materials and Methods. Again the left-most lane represents time 0, with additional lanes representing increments as in (A). Reactions involving C320 omitted the 5 min time point.