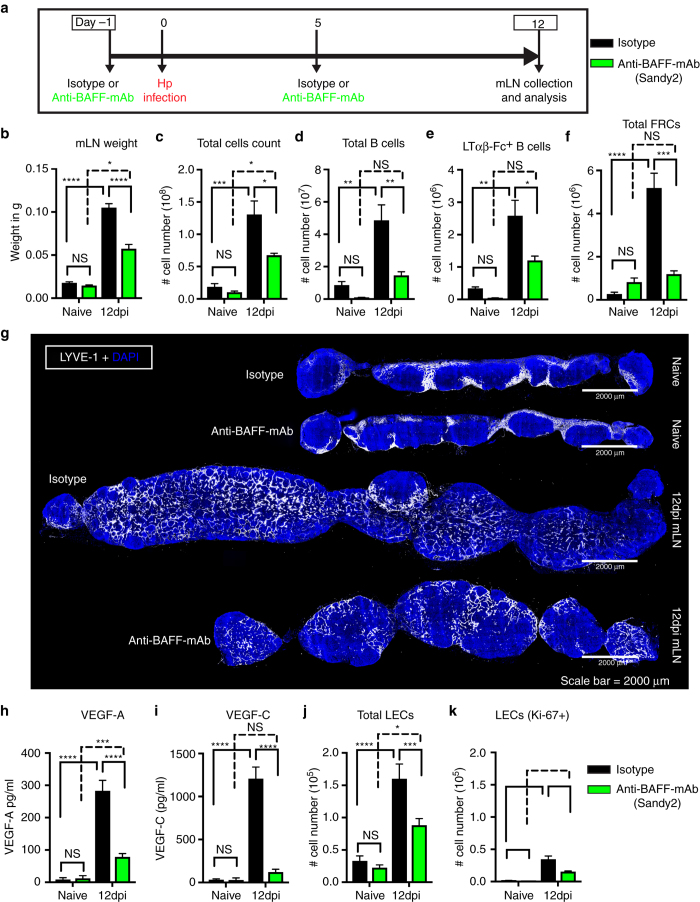
Fig. 7.
In vivo BAFF inhibition attenuates helminth-induced lymphangiogenesis. a C57BL/6 J wild-type mice were treated with isotype control or anti-BAFF mAb (Sandy-2) and infected with Hp. The entire chain of the mLN was collected at 12 dpi and processed for flow cytometry or histological staining. b Total weight of mLN, c total cell count, d total number of B cells, e absolute number of lymphotoxin-expressing B cells, and f total FRCs (PDPN+MadCAM1−CD31−) present within the mLN as determined using flow cytometry. g mLN serial cryosections showing lymphatic organization after treatment with isotype control or anti-BAFF mAbs in naive or at 12 dpi mice (blue; DAPI, grays; LYVE-1+ LECs). Scale bar = 2000 μm. Images are from a single mouse and are representative of two independent experiments each including n ≥ 2 mice/group/time point. h VEGF-A and i VEGF-C in mLN tissue homogenates as determined by ELISA. j, k total LECs (PDPN+CD-31+) and proliferating LECs (PDPN+CD-31+Ki-67+) in the mLN of naive and 12 dpi mice treated with isotype control or anti-BAFF mAbs were determined using flow cytometry. Data represent mean ± SEM and representative of two independent experiments with n = 3mice/group/time-point. Statistical analyses were performed using ANOVA, Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test and significance donated as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001