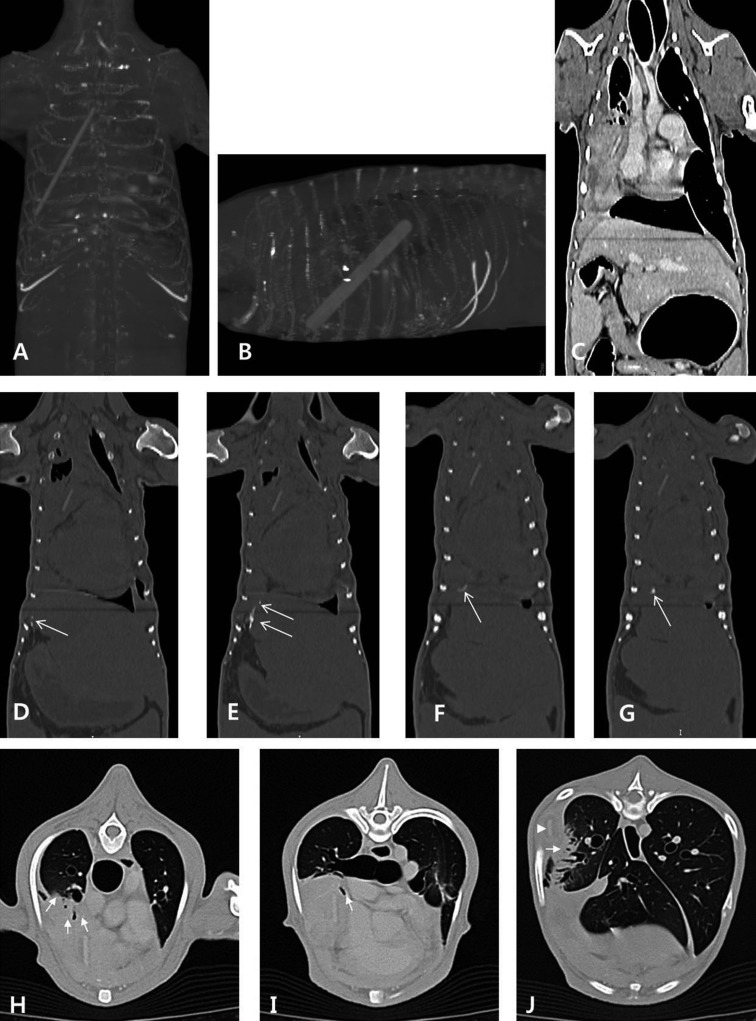
Fig. 3.
Thoracic and abdominal computed tomography scans. A–G: Intrathoracic foreign body and evidence of its extraluminal migration path are detected. A, B. The linear hyperattenuating foreign body is located in the right thoracic cavity between the third and ninth ribs. The length is 100.75 mm, and it extends in the caudodorsal direction from a cranioventral origin. C. The right diaphragm is displaced forward. D–G. Dorsal computed tomographic view in a bone window shows several hyperattenuating spots thought to be calcified (arrows) cranial to the gastric pylorus leading to the diaphragm. H–J: Right-side pulmonary consolidations are observed. H. The ventral part of the right cranial lung lobe is partially consolidated (arrows). I. The right middle lung lobe is collapsed with complete bronchial obstruction (arrow). J. Partial consolidation (arrow) is detected in the right caudal lung lobe near the foreign body (arrowhead).