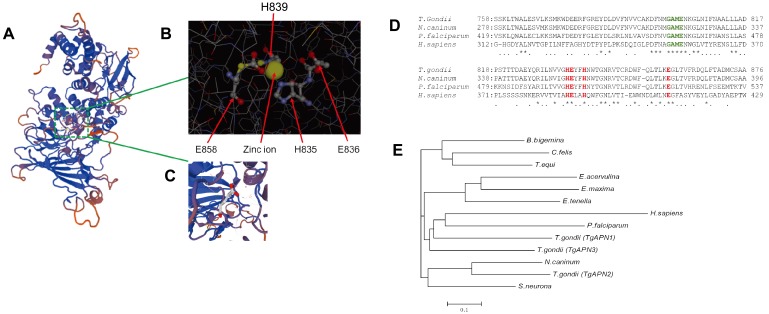
Fig. 1.
Structural prediction and evolutionary tree of TgAPN2. (A) The spatial protein structure was predicted using the SWISS-MODEL. (B) Residues H835, E835, H839 and E858 constitute the “HEXXH” domain of M1 aminopeptidases. Ligand: zinc ion. (C) Glutamic acid (1×). (D) Multiple-sequence alignment of the active sites (boxed region) and flanking amino acid sequences of proteins from the M1 protease family, including T. gondii APN, P. falciparum A-M1, N. caninum APN, and H. sapiens APN. TgAPN2 contains the “GAME” and “HEXXH” functional domains of the M1 protease family. (E) Evolutionary tree of TgAPN2. The predicted sequences of enzymes from T. gondii, C. felis, E. acervuline, E. maxima, B. bigeminy, and N. caninum APN1 enzymes were obtained from the ToxoDB database (http://toxodb.org/toxo/). Sequences of the E. tenella N1, P. falciparum, and H. sapiens enzymes were obtained from the NCBI protein database (accession numbers are given in parentheses). TgAPN2 was similar to APN from N. caninum (44.9% identity) and S. neurona (34.5% identity); the homology between TgAPN2 and PfA-M1 was relatively low, only 20%.