Figure 4.
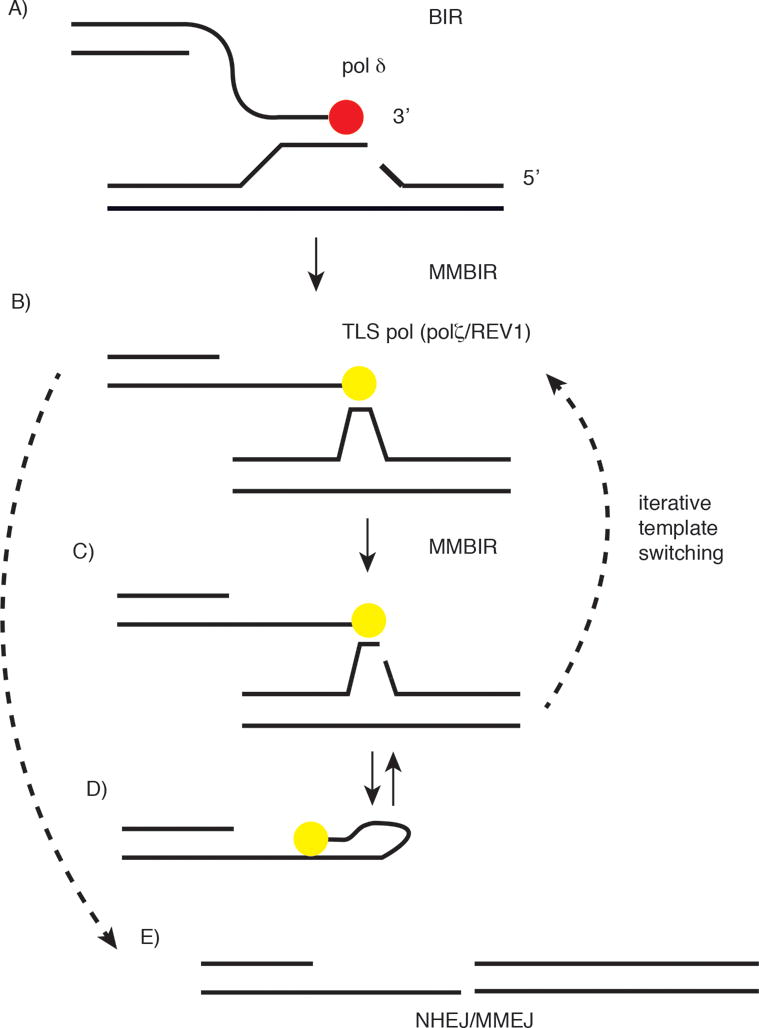
Template switching and the transition from BIR to MMBIR. A) Fork stalling within or beyond microsatellite sequences causes fork collapse/breakage. B) TLS polymerases (Polζ/Rev1) enable microhomology-mediated BIR (MMBIR). TLS polymerase synthesis is not processive and fork collapse leads to template switching and microhomology-mediated BIR at a new site. C) Successive cycles of fork stalling and template switching (FoSTeS) lead to complex genomic rearrangements (CGRs). D) Self-annealing and DNA synthesis at microhomologies in nascent DNA. E) DSBs at simultaneously broken microsatellites may recombine by nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) or microhomology-mediated end joining (MMEJ).
