Figure 1.
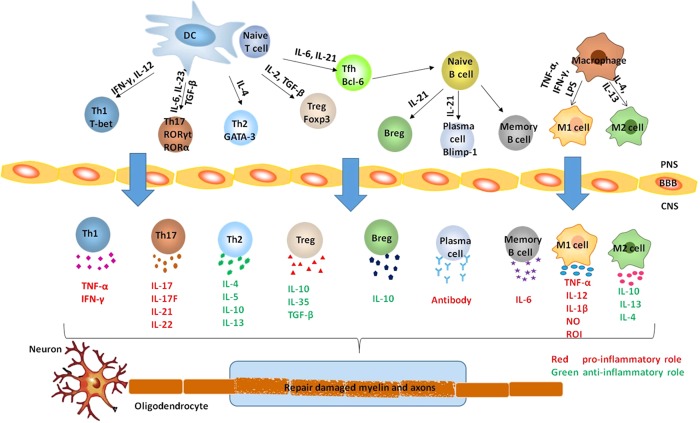
Pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. In the peripheral immune system, naive CD4 + T cells can differentiate into effector T helper cells depending on the cytokines, such as IL‐12, IL‐6, and TGF‐β, that secrete by APCs (macrophages, DCs, and B cells) together with costimulatory molecules (CD40, CD80, CD86) present on APCs. Effector T cells cross the BBB into the CNS. Activated T cells and macrophages with M1 type are proinflammatory and promote demyelination, axonal damage, and the formation of disease plaques, while macrophages with M2 type and Tregs have anti‐inflammatory, regulatory properties and inhibit disease progression by facilitating tissue repair. At the same time, with the help of Tfh cells, B cells differentiate into plasma cells and memory B cells. Plasma cells produce antibodies, which attack the myelin sheath on neurons. On the other hand, B cells promote both pathogenic and protective mechanisms by producing cytokines such as IL‐6 and IL‐10 in MS. APC indicates antigen‐presenting cell; BBB, blood‐brain barrier; Th, T helper; Treg, regulatory T; Tfh, follicular helper CD4+T; Breg, regulatory B; IL, interleukin; Bcl‐6, B cell lymphoma 6; Foxp3, forkhead box P3; GATA‐3, GATA‐binding protein 3; IFN‐γ, interferon‐γ; RORγt, retinoid‐related orphan receptor γt; RORα, retinoid‐related orphan receptor α; T‐bet, T‐box transcription factor; TGF‐β, transforming growth factor‐β; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; M1 cells, classically activated macrophages; M2 cells, alternatively activated macrophages; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NO, nitric oxide; ROI, reactive oxygen intermediates. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
