Figure 2.
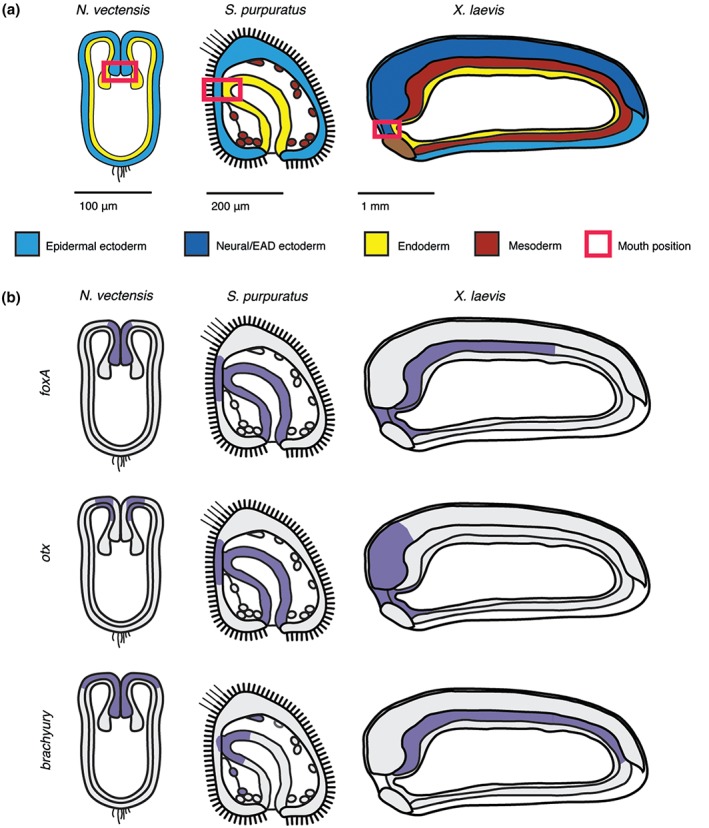
Mouth forms where ectoderm and endoderm are juxtaposed. (a) Position of future mouth relative to germ layers in embryos of three representative animals. Schematics of sagittal sections are shown for the diploblast cnidarian Nematostella vectensis (invertebrate), the triploblasts and deuterostomes sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (invertebrate) and frog Xenopus laevis (vertebrate). The red box outlines the mouth‐forming region made up of juxtaposed ectoderm and endoderm. In vertebrates, this region is termed the extreme anterior domain. (b) Ancestral mouth embryonic gene expression domains in N. vectensis, S. purpuratus, and X. laevis (purple). The mouth expression domain of foxA and otx but not brachyury is conserved in vertebrates.
