Figure 3.
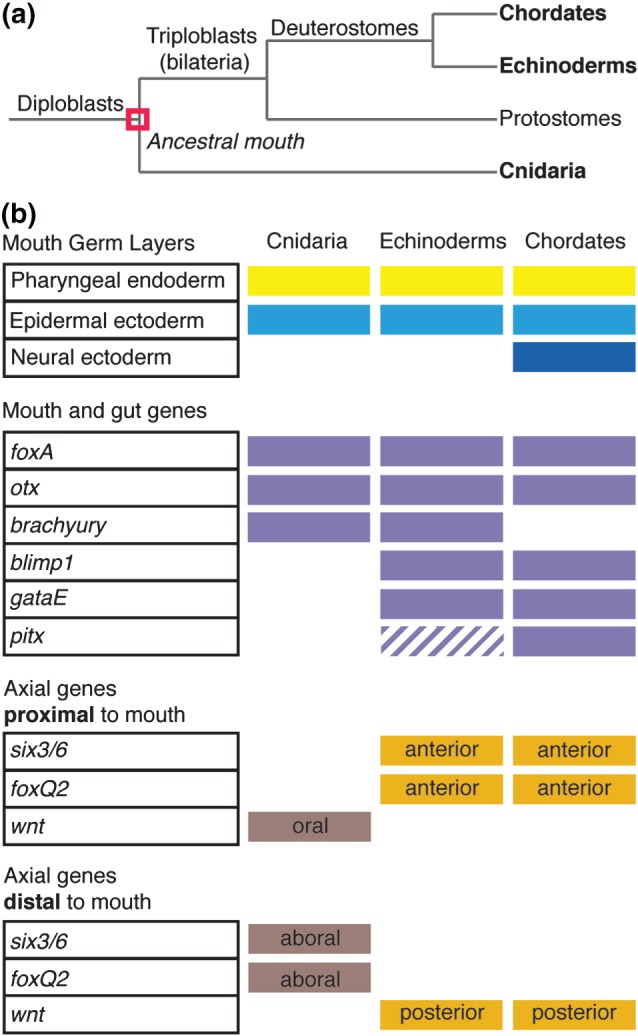
Ancestral mouth was present in the common ancestor of cnidaria and triploblasts. (a) Phylogenetic tree. Chordates, echinoderms, and cnidaria are three distantly related phyla that retain common mouth characteristics, suggesting that the mouth evolved once. (b) Criteria used to evaluate mouth evolution. The mouths of cnidaria, echinoderms, and chordates are all comprised of ectoderm and endoderm and express foxA and otx. There are phylum‐specific characteristics such as neural ectoderm contributing to the chordate mouth and the expression of blimp1, gataE, and pitx in echinoderm and chordates. Analysis of axial positioning genes demonstrates that the cnidarian oral–aboral axis is equivalent to the echinoderm and chordate posterior–anterior axis.
