Figure 1.
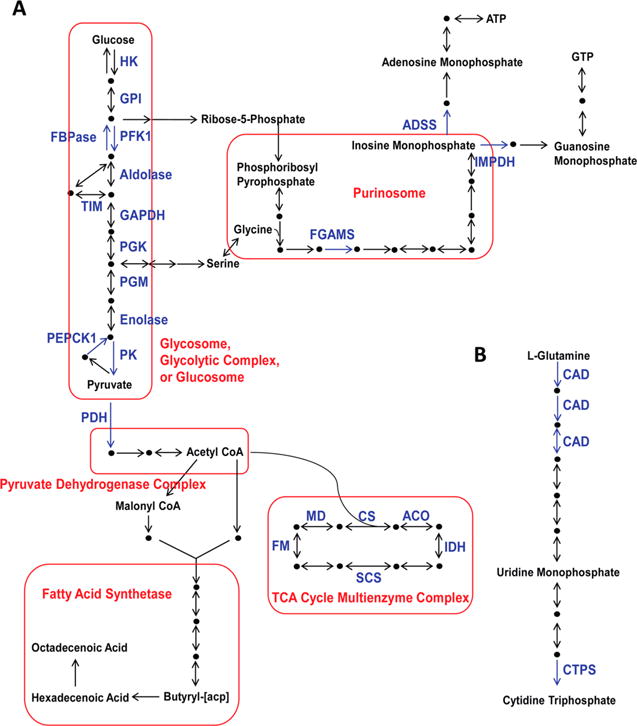
An overview of central carbon metabolism. Enzymes extensively discussed in this review are named in blue, while discussed multienzyme complexes are boxed in red. Metabolites are either shown by their names or black dots. (A) Glucose is consumed through the central pathway of glycolysis, or generated by gluconeogenesis, which shuttles into energy metabolism and anabolic biosynthetic pathways. The product of glycolysis, pyruvate, is shuttled to the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Then, the produced acetyl-CoA is directed to either fatty acid synthetase, or the TCA cycle protein complex. Meanwhile, ribose-5-phosphate and serine are produced from glycolytic intermediates and shunted into de novo purine biosynthesis, which is promoted by the purinosome. (B) L-Glutamine is converted to cytidine triphosphate through de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis. Used acronyms: hexokinase (HK); glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI); phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK1); fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase); triose phosphate isomerase (TIM); glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH); phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK); phosphoglycerate mutase (PGM); phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK); pyruvate kinase (PK); pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH); formylglycinamidine ribonucleotide synthase (FGAMS); inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH); adenylosuccinate synthetase (ADSS); citrate synthase (CS); acetyl-CoA oxidase (ACO); isocitrate dehydrogenase (DH); succinyl-CoA synthetase (SCS); fumarase (FM); malate dehydrogenase (MD); carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase, aspartate transcarbamylase, and dihydroorotase (CAD); cytidine triphosphate synthase (CTPS).
