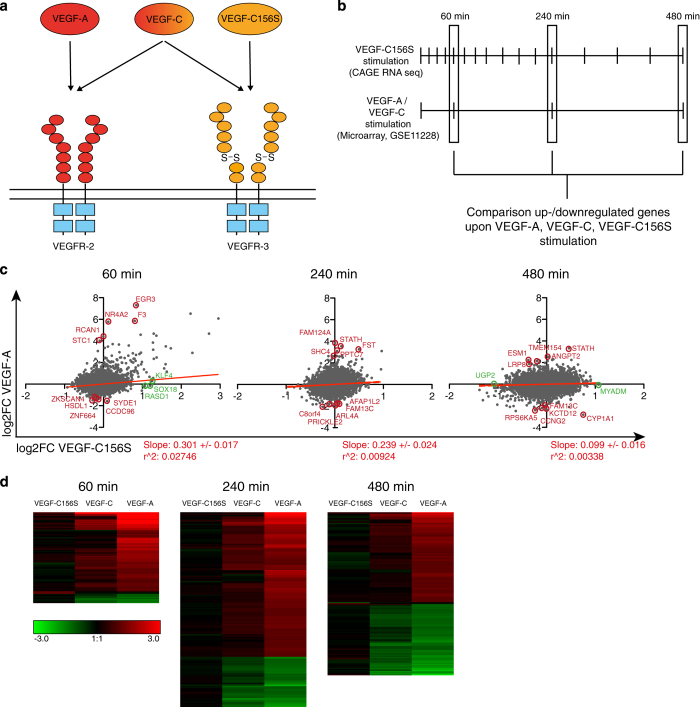
Figure 3. Differential gene regulation by VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 in LECs.
(a) Schematic representation of the binding abilities of VEGF ligands to VEGFR-2 and -3. VEGF-A binds to VEGFR-2 exclusively, whereas fully mature, wildtype VEGF-C can act on both VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3. VEGF-C with a Cys156=>Ser mutation acts as a selective VEGFR-3 agonist. (b) Schematic illustration of the three time course gene expression data sets used for the analysis. CAGE RNA sequencing of LECs stimulated with VEGF-C156S was performed at 16 different time points over a course of 480 min. The 60, 240 and 480 min time points were compared with previously published microarray based gene expression data of LECs stimulated with VEGF-A or mature wildtype VEGF-C. (c) Correlation of log2FC of all matchable genes induced by VEGF-A (y-axes) and VEGF-C156S (x-axes) in LECs at the 60, 240 and 480 min time point. Linear regression and Pearson correlation coefficients are indicated in red. The most differentially regulated genes (up to 5) are indicated in dark red (genes up- or downregulated by VEGF-A but not by VEGF-C156S) and green (genes up- or downregulated by VEGF-C156S but not by VEGF-A). (d) Genes were considered as differentially regulated by VEGF-C156S and VEGF-A if they were strongly regulated by at least one of the ligands (P<0.05, log2FC>1 or <−1), and if the difference in log2FC values after VEGF-A and VEGF-C156S stimulation was at least four-fold. The heat maps show the log2FC values of all differentially regulated genes after VEGF-C156S, wildtype VEGF-C and VEGF-A stimulation.