Figure 2. Figure showing the rationale of treatment recommendations.
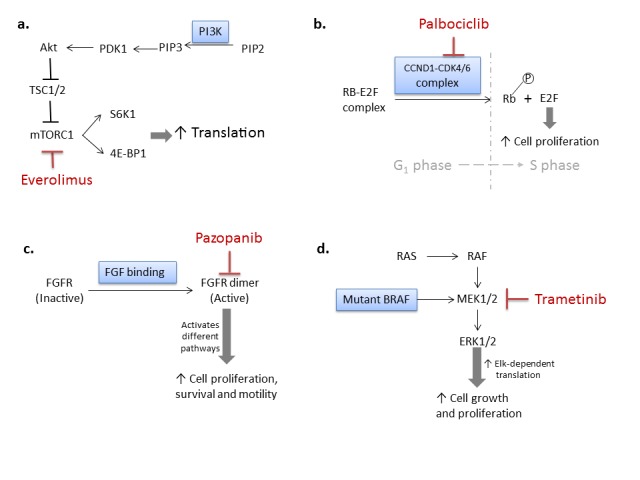
Simplified signaling pathways with treatment targets related to the patient are presented in this figure. Molecular aberrations are placed in the blue boxes. Drugs are presented in red. a) Everolimus as a mTROC1 inhibitor targets the bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA) aberrations. b) Cyclin D1 (CCND1) amplification promotes G1/S transition through releasing E2F by phosphorylating retinoblastoma protein (Rb). Palbociclib functions to block the G1/S transition by blocking cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) kinase activity, which relies on wild-type, fully functioning Rb. c) When retinoblastoma protein-RB1 mutation was caught on circulating tumor deoxyribonucleic acid (ctDNA), pazopanib took the place of palbociclib in the regimen, as a fibroblast growth factor (FGFR) inhibitor, targeting the FGF3/4/19 amplifications. d) Mutant BRAF in the kinase domain indicates an elevated RAS-RAF pathway. Trametinib is suggested to block MEK1/2 activity when allele frequency of the BRAF kinease domain mutation increased in ctDNA.
