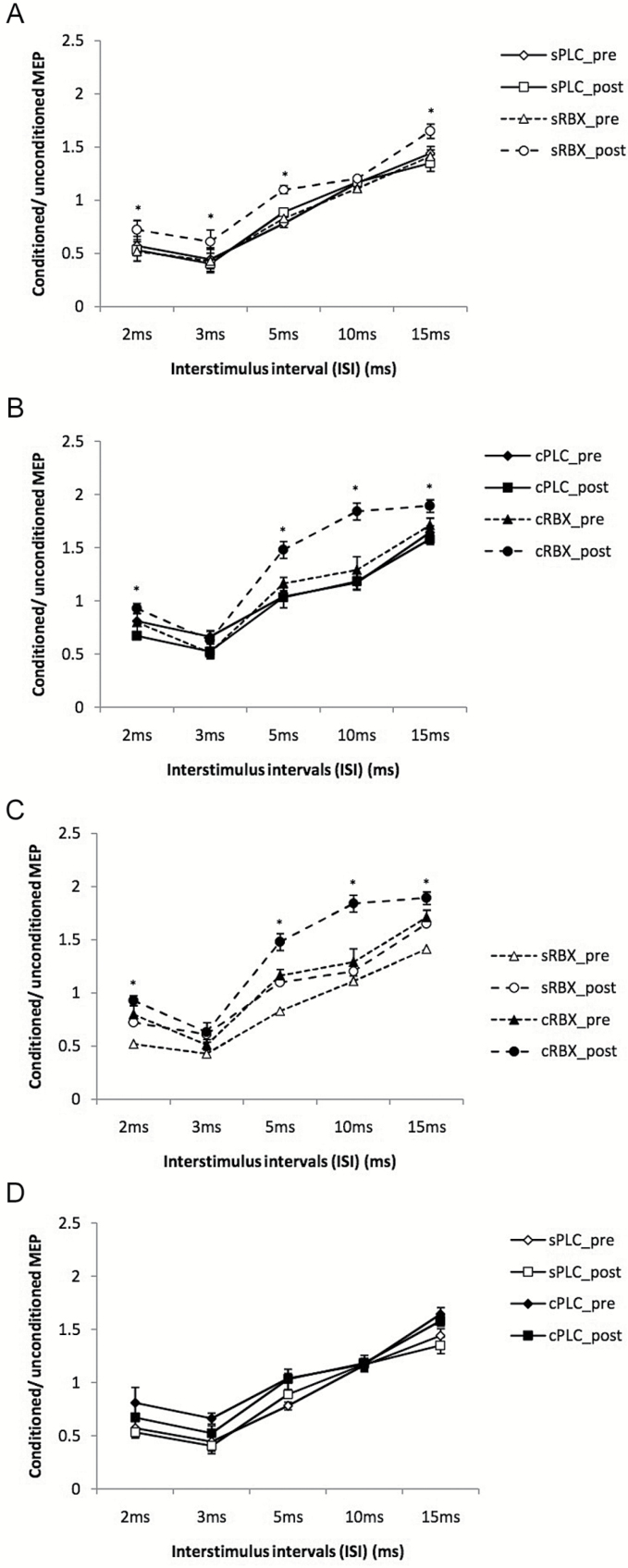
Figure 3.
Short-latency intracortical inhibition and intracortical facilitation before and after drug administration. Single-pulse standardized double stimulation MEP amplitude ratios ± SEM are depicted for ISIs revealing inhibitory (ISIs of 2, 3, and 5 ms) and facilitatory (ISIs of 10 and 15 ms) effects for different medication conditions: single-dose placebo (sPLC), single-dose RBX (sRBX), chronic reboxetine+placebo medication at the day of experiment (cPLC), and chronic reboxetine+reboxetine at the day of experiment (cRBX). (A) The sRBX post condition significantly increased facilitation for the ISI of 15 milliseconds and decreased inhibition for ISIs of 2, 3, and 5 milliseconds compared with sPLC post condition. (B) cRBX post showed a significant increase of facilitation for the ISIs of 10 and 15 milliseconds and a significant decrease of inhibition for the ISI of 3 and 5 milliseconds compared with cPLC post. (C) cRBX post showed significant facilitation for the ISIs of 10 and 15 milliseconds and significant decrease of inhibition for the ISIs of 2 and 5 milliseconds compared with sRBX post. (D) cPLC post showed a nonsignificant trend towards enhanced facilitation and decreased inhibition compared with sPLC post. Asterisks indicate significant differences (Student’s t test, P<.05). Vertical bars depict SEM.