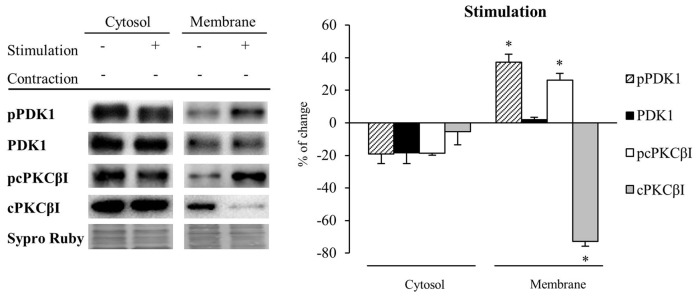
Figure 5.
Synaptic activity increases pPDK1 and PCKβI in the membrane fraction of skeletal muscle. Western Blot of PDK1 and pPDK1 after isolation of membrane and cytosol fractions in presynaptic stimulation treatment at 1 Hz stimulation for 30 min. Presynaptic stimulation has been simplified as Stimulation. Each column has been compared to its respective control (see Table 1). Results showed that synaptic activity does not affect significantly the level of any protein in the cytosol. Therefore, the ratios pcPKCβI/cPKCβI and pPDK1/PDK1 remain the same. However, both pPDK1 and its substrate, pcPKCβI were significantly increased in the membrane fraction. Thus, both ratios pcPKCβI/cPKCβI and pPDK1/PDK1 were increased indicating that synaptic activity specifically enhances phosphorylation of PDK1 and cPKCβI. Data are mean percentage ± SEM, *p < 0.05 (n = 5). Abbreviations: phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1; pPDK1, phosphorylated phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1; cPKCβI, conventional protein kinase C βI; pPKCβI, phosphorylated conventional protein kinase C βI.