Figure 2.
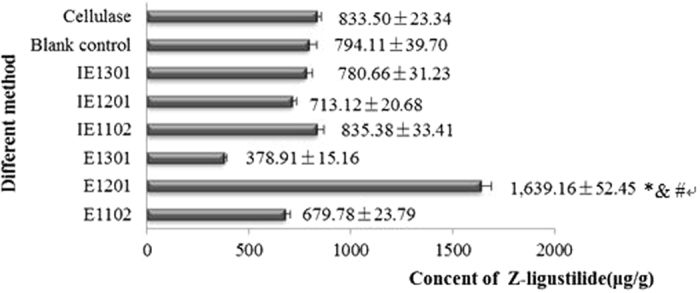
Comparison of different methods for extracting Z-ligustilide from A. Sinensis. In here, RAS powder was pretreat with different cellulase for 30 h at 37 °C, and then reflux extraction was performed and the concentration of Z-ligustilide was determined by HPLC. Furthermore, the numbers 1102, 1201 and 1301 represents the three identified endophyte bacterial strains: No.Lut1102, No.Lut1201 and No.Lut1301, respectively. E corresponds to the respective cellulase produced by the bacteria. IE represents the inactivated enzymes of the corresponding reference; blank was without any enzyme treatment using the traditional extraction method. Cellulase represents commercially available cellulase assisted extraction of Z-ligustilide *,&,#p < 0.05 compared with commercially available cellulases, blank and inactivate enzyme control groups.
