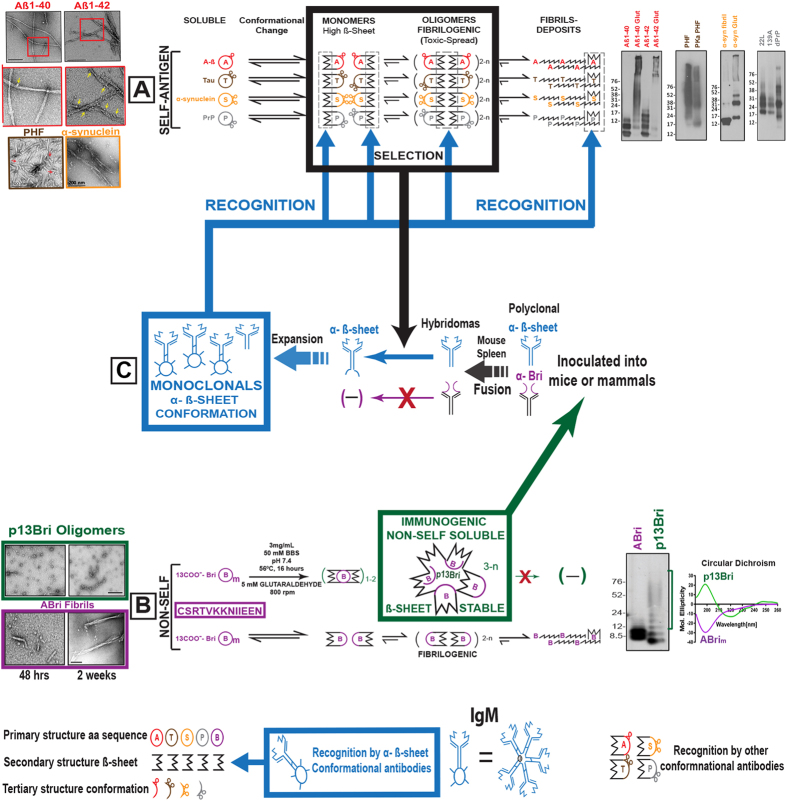
Figure 1.
Production of anti ß-sheet secondary structure conformational monoclonal antibodies with specificity to oligomeric toxic conformers present in neurodegenerative diseases (NDD). (A) Color coded pathways to oligomeric forms and fibrillar deposits of self-antigenic protein/peptides associated with pathology on most common NDD: Aß (red) and tau (brown) for Alzheimer’s Disease; α-synuclein (orange) for Lewy Body diseases, and PrP (grey) for prionoses. Black shape represents common to all ß-sheet secondary structure acquired during pathological conformational change. Electron microscopy (EM) of oligomers and fibrils on the left and immunoblots of oligomeric forms detected by specific antibodies on the right, all color coded (also in Figs 2, 3 and 4). (B) One letter code of the 13 amino acids sequence of the non-self ABri peptide (purple boxed). Bottom pathway shows the normal conversion of ABri peptides to oligomers and fibrils (purple). Top pathway shows the controlled polymerized reaction with glutaraldehyde (see methods) leading to p13Bri the immunogenic, non-self, soluble and stable ß-sheet oligomers of 10–100 kDa molecular weight (from purple to green frame). Black shapes represent common to all ß-sheet structure. On the left, EM of the oligomeric p13Bri (green frame) and the oligomer/fibrils of the aged ABri peptide (purple frame). On the right Immunoblot with rabbit polyclonal anti-Bri and circular dichroism analysis of both forms (color coded and also in Supplementary Fig. 2). (C) The p13Bri (green boxed) inoculated into mice to produce hybridomas (Methods and Table 1); horizontal blue arrows show the selection process of monoclonals by the oligomeric β-sheet conformers of (A) antigens (thick black frame and arrow); framed in blue the selected anti-conformational monoclonal antibodies that recognize ß-sheet secondary structure common to (A) and (B) pathways. The thick blue arrows from the framed blue antibodies signal possible interactive sites with pathological conformers on NDD (also in Figs 3, 4 and 5).