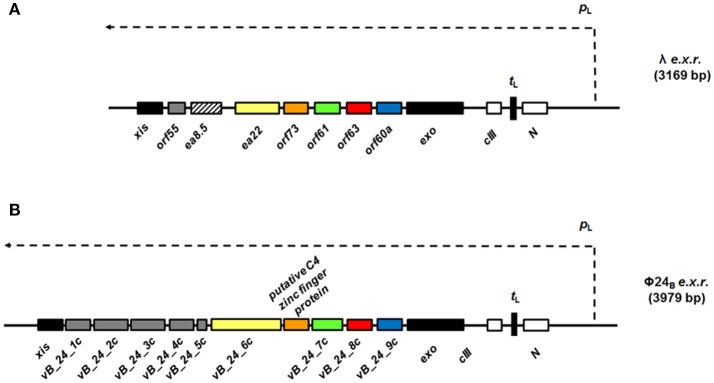
Figure 1.
Maps of genes and open reading frames (ORFs) from the region located between exo and xis genes (black rectangles), the exo-xis region or e.x.r., of lambdoid bacteriophages: λ (A) and Φ24B (B). In the case of phage λ (A), the exo-xis region consists of two recognized genes: ea22 and ea8.5, and five additional ORFs, named: orf60a, orf63, orf61, orf73, and orf55, which expression is under control of the pL promoter (thin dashed arrow). Comparatively, the exo-xis region of phage Φ24B (B) contains additional ORFs (gray rectangles), but there is no homolog of the ea8.5 gene of phage λ (A), rectangle with black stripes). Note, that some ORFs from the exo-xis region of phage Φ24B (B): vb_24B_9c (blue rectangles), vb_24B_8c (red rectangles), vb_24B_7c (green rectangles), putative C4 zinc finger protein (orange rectangles), and vb_24B_6c (yellow rectangles) are homologs of phage λ orf60a, orf63, orf61, orf73, ea22 (B), respectively. In spite of the differences in composition of both λ and Φ24B exo-xis regions, attention needs to paid to highly conserved sequences of the orf60a-orf73 regions among lambdoid bacteriophages (≥70% nucleotide and amino acid sequence identity) (Bloch et al., 2013). The regulatory genes: N and cIII are marked as white rectangles and tL terminator is indicated as black vertical rectangle.