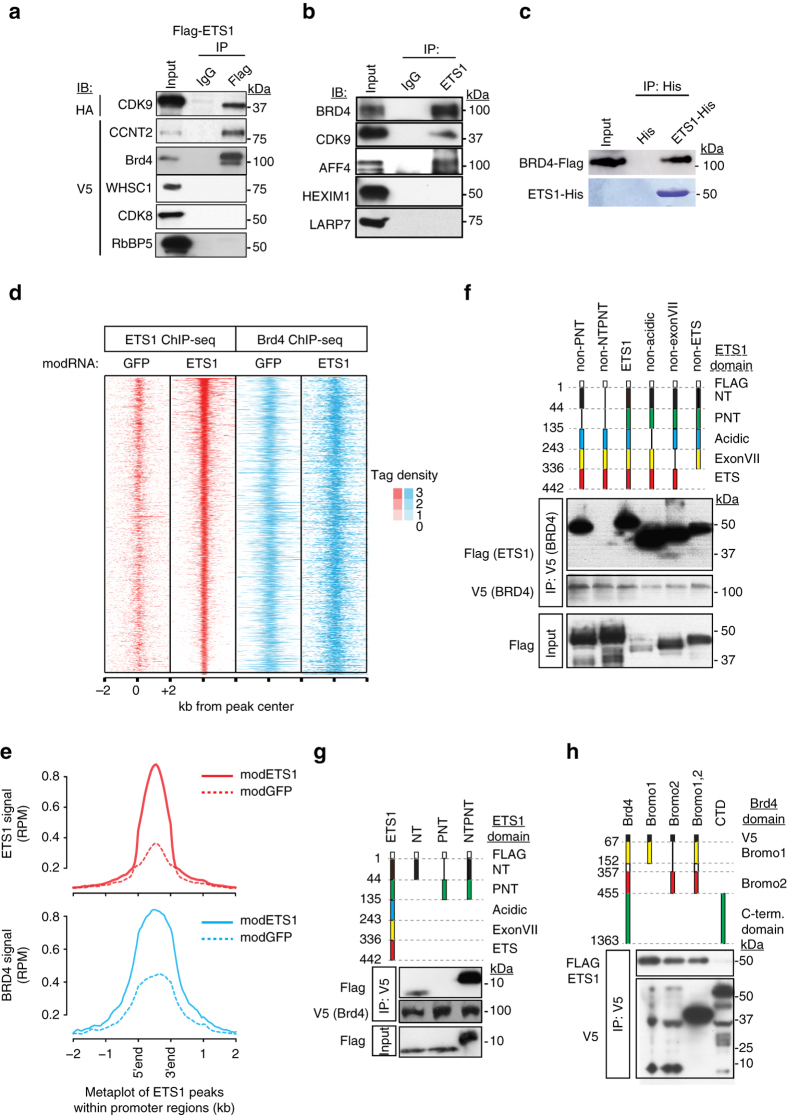
Fig. 3.
ETS1 recruited P-TEFb to chromatin by direct interaction with BRD4. a ETS1 co-precipitated P-TEFb and BRD4. 293T cells were co-transfected with indicated expression constructs. ETS1 was immunoprecipitated (FLAG), and interacting proteins were detected with HA or V5 antibodies. b ETS1 interacted with active P-TEFb in HUVEC cells. Endogenous ETS1 was immunoprecipitated, and endogenous interacting proteins were detected using specific antibodies. c Bacterially expressed, affinity purified ETS1-His bound in vitro transcribed and translated BRD4. d ETS1 and BRD4 promoter co-occupancy. HUVEC cells were transfected with ETS1 or GFP modRNA, and ETS1 and BRD4 chromatin occupancy was measured by ChIP-seq. The tag heatmap displays ETS1 and BRD4 signals from ETS1 regions within promoters. ETS1 and BRD4 co-occupied promoters, and increased ETS1 occupancy correlated with increased BRD4 occupancy. e Aggregation plots of ETS1 and BRD4 signals shown in d. f, g BRD4 binds the ETS1 NT domain. FLAG-tagged ETS1 expression constructs containing the indicated domains were co-transfected into 293T cells with V5-tagged BRD4. ETS1 deletion mutants were detected in BRD4 (V5) immunoprecipitates by FLAG immunoblotting. The NT domain was required for BRD4 binding. h BRD4 Bromo domains bind ETS1. V5-tagged expression constructs containing the indicated BRD4 domains were co-transfected into 293T cells with FLAG-tagged ETS1. BRD4 (V5) immunoprecipitates were probed for interacting ETS1 protein by FLAG immunoblotting. Either bromodomain of BRD4 was sufficient for ETS1 interaction