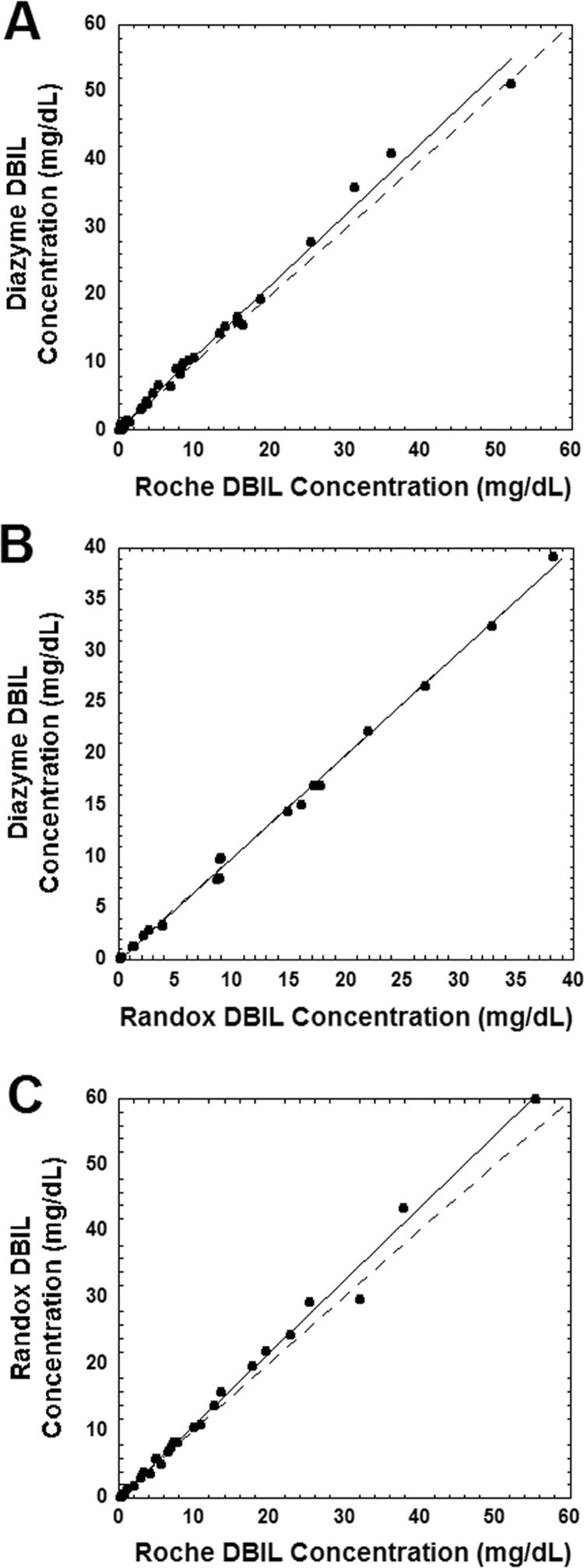
Fig. 1.
Correlation between the DBIL assays for samples with hemolysis index of less than 30. The dashed line in the three plots indicates the line of identity, while the solid line is from linear regression. Slope and y-intercept are presented with 95% confidence intervals in parentheses. (A) Comparison of the Diazyme vanadate oxidase DBIL assay with the Roche Diagnostics diazo DBIL assay (n=38). Linear regression statistics: r2=0.992, slope=1.05 (1.02, 1.08), y-intercept =0.26 (−0.19, 0.71). Slope was significantly greater than 1.0 (p<0.01). (B) Comparison of the Randox and Diazyme DBIL assays (n=27). Linear regression statistics: r2=0.998, slope=1.00 (0.98, 1.02), y-intercept =0.08 (−0.35, 0.18). (C) Comparison of the Roche and Randox DBIL assay (n=29). Linear regression statistics: r2=0.993, slope=1.09 (1.05, 1.12), y-intercept =0.10 (−0.50, 0.71). Slope was significantly greater than 1.0 (p<0.01). DBIL in mg/dL may be converted to µmol/L by multiplying by 17.1.