Figure 3.
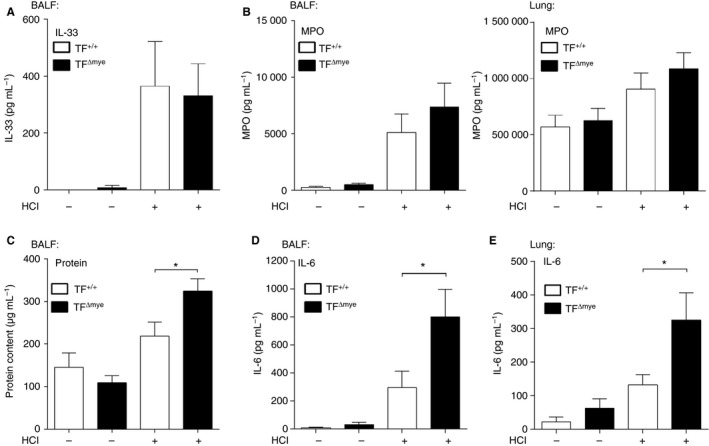
Increased inflammation in myeloid tissue factor (TF)‐deficient mice in response to acid‐induced acute lung injury (ALI). (A–D) Interleukin (IL)‐33 (A) (n control TF +/+ = 6, n control TF Δmye = 5, n HC l TF +/+ = 7, n HC l TF Δmye = 8), myeloperoxidase (MPO) (B) (bronchoalveolar lavage fluid [BALF] – n control TF +/+ = 6, n control TF Δmye = 4, n HC l TF +/+ = 11, n HC l TF Δmye = 12; lung – n control TF +/+ = 5, n control TF Δmye = 5, n HC l TF +/+ = 14, n HC l TF Δmye = 14) and IL‐6 (D) (n control TF +/+ = 6, n control TF Δmye = 5, n HC l TF +/+ = 10, n HC l TF Δmye = 12) were measured in BALF by ELISA. (C) The protein content in BALF was measured with a bicinchoninic acid protein assay (n control TF +/+ = 3, n control TF Δmye = 3, n HC l TF +/+ = 7, n HC l TF Δmye = 10). (E) IL‐6 levels in total lung tissue were determined by ELISA (n control TF +/+ = 7, n control TF Δmye = 8; n HC l TF +/+ = 11, n HC l TF Δmye = 13). Parameters were analyzed 8 h after HCl treatment. For statistical analysis, unpaired Student's t‐tests (A–E) were performed; *P < 0.05. Littermate‐controlled experiments were performed.
