Figure 7.
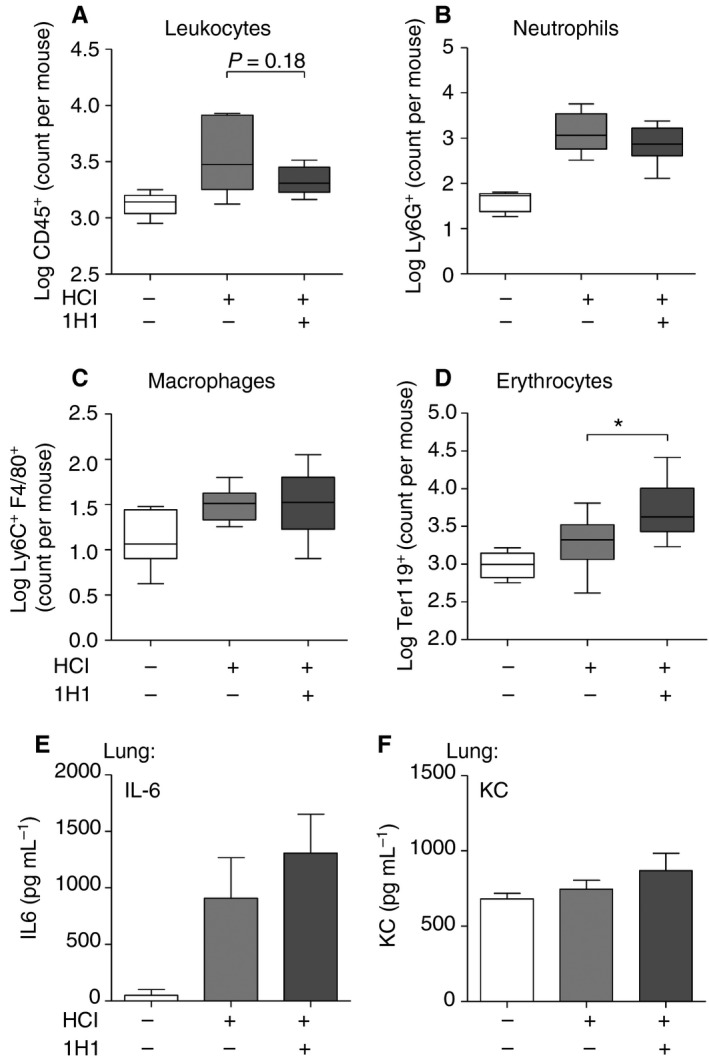
Systemic tissue factor (TF) inhibition in acid‐induced acute lung injury (ALI). Wild‐type mice were intraperitoneally injected with anti‐TF blocking antibody (1H1) or vehicle prior to HCl treatment, and parameters were analyzed 8 h after HCl treatment. (A–D) Extravasation of (A) leukocytes (CD45+), (B) neutrophils (CD45+ Ly6G+ F4/80−), (C) macrophages (CD45+ F4/80+) and (D) erythrocytes (Ter119+) in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was determined by flow cytometry. (E, F) Interleukin (IL)‐6 (E) and chemokine (C‐X‐C‐motif) ligand‐1 (KC) (F) levels in BALF were determined by ELISA. (A) n control WT = 5; n HC l WT = 12; n HC l 1H1 = 9. (B) n control WT = 5; n HC l WT = 8; n HC l 1H1 = 8. (C) n control WT = 7; n HC l WT = 8; n HC l 1H1 = 8. (D) n control WT = 7; n HC l WT = 10; n HC l 1H1 = 10. (E, F) n control WT = 3; n HC l WT = 6; n HC l 1H1 = 6. For statistical analysis, unpaired Student's t‐tests were performed; *P < 0.05. Littermate‐controlled experiments were performed.
