Figure 1.
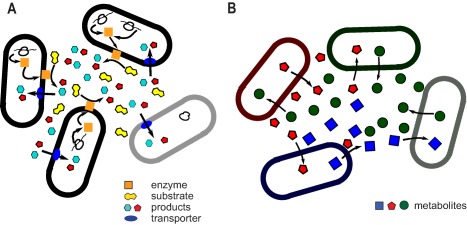
A. Interactions based on shared public goods. Some cells (cooperators, shown in black edge) produce an enzyme required to split a substrate into digestible products. Other cells (cheats, shown in grey), do not produce the enzyme but take advantage of the public goods produced by the others.
B. Interactions based on cross‐feeding. Some cells in the community excrete metabolites that can be taken up by other cells giving rise to a web of interactions.
