Fig. 2.
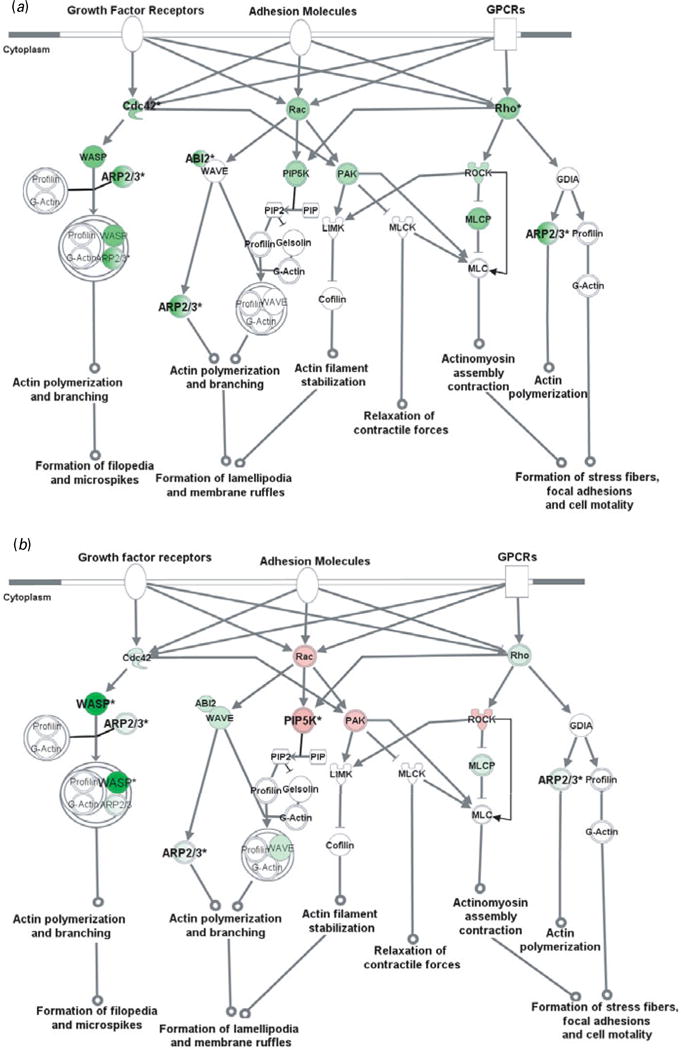
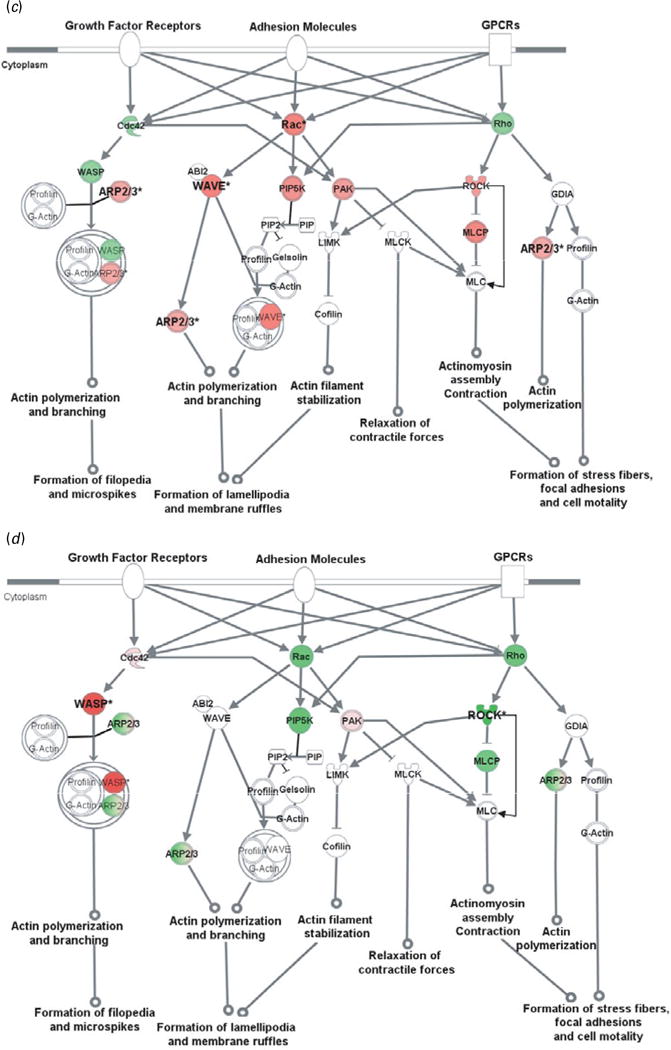
Cell adhesion molecules modulate actin cytoskeleton via Rho small GTPases. Genes in red were up-regulated whereas those in green were down-regulated at the mRNA level by gestation nicotine exposure in (a) the caudate putamen, (b) nucleus accumbens, (c) prefrontal cortex and (d) amygdala. * Significantly modified compared with gestational saline treatment (p<0.05 at least). ABI2, abl-interactor 2; ARP2/3, actin-related protein complex; Cdc42, cell division cycle 42; Cofilin, cofilin 1 (non-muscle); GDIA, Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) alpha; Gelsolin, gelsolin (amyloidosis, Finnish type); LIMK, LIM domain kinase 1; MLC, myosin light chain; MLCK, myosin light chain kinase; MLCP, myosin light chain phosphatase; PAK, p21-activated protein kinase 1 (Pak1); PIP, 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4-phosphate; PIP2, 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PIP5K, 1-phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase; Rac, ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1); Rho, ras homolog gene family, member A (RhoA); ROCK, Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 (Rock1); WASP, Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome-like (N-WASP); WAVE, WAS protein family.
