Fig 3. TLR4 on hematopoietic cells is critical for oxaliplatin-induced mechanical hyperalgesia.
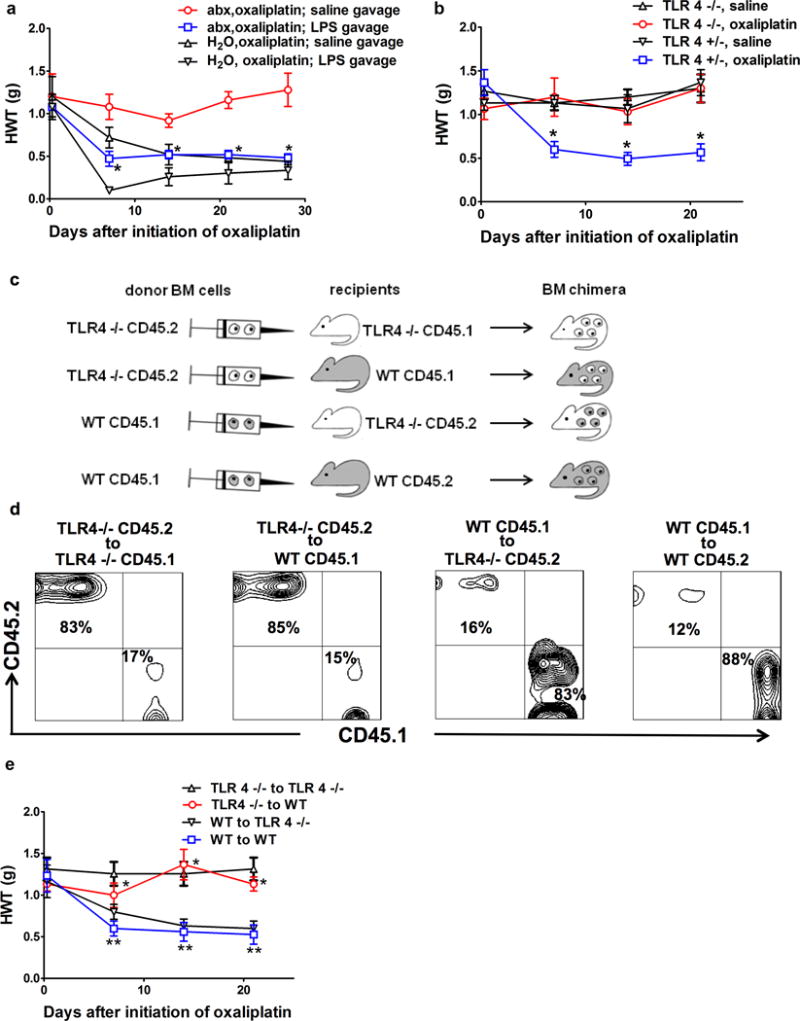
a) Exogenous administration of LPS through gastric gavage reversed the effect of gut microbiota eradication. Mice were fed with antibiotic water (abx) or regular water (H2O), followed by oxaliplatin injection. LPS (3mg/Kg) or normal saline was administered on days of oxaliplatin injection and twice weekly afterwards. *p<0.05, abx,oxaliplatin; LPS gavage vs. abx, oxaliplatin; saline gavage, N=7 each group. b) Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) knockout mice did not develop oxaliplatin-induced mechanical hyperalgesia. TLR4 knockout (TLR4−/−) or littermate heterozygous (TLR 4+/−) mice were treated with oxaliplatin or saline and were examined at indicated time points for hindpaw mechanical withdrawal threshold (HWT) (N=6 each group). * p<0.05 WT, oxaliplatin vs. all other groups. c–d) Generation of bone marrow (BM) chimeras. c) Flow chart for BM chimeric mice generation. Recipients were irradiated 500 Rad × 2 followed by bone marrow cells injection. Donor bone marrow cells were derived from TLR4−/− or WT mice, and were injected to WT or TLR4−/− recipients, using a cross-over study design. CD 45.1 and CD45.2 congenic markers were used to distinguish between donor-derived and recipient-derived hematopoietic cells. d) Confirmation of successful generation of bone marrow chimera. Fourteen weeks after BM transplantation, DRG samples were collected and stained for CD45.1 and CD45.2 congenic markers. Contour plots were gated on CD11b+ and CD3− cells. Each panel represents 6 independent stainings. e) TLR4 on hematopoietic cells is critical for oxaliplatin-induced mechanical hyperalgesia. BM chimeric mice generated as shown in c–d) were treated with oxaliplatin (N=6 each group). In TLR4−/− to WT group, hematopoietic cells were from TLR4−/− donors. These mice were protected from oxaliplatin-induced mechanical hyperalgesia despite the presence of TLR4 on host-derived radio-resistant cells. *p<0.05 TLR4−/− to WT vs. WT to WT. In contrast, in WT to TLR4−/− group, hematopoietic cells were from WT donors, these mice developed oxaliplatin-induced mechanical hyperalgesia despite the absence of TLR4 on host-derived radio-resistant cells. ** p> 0.05 WT to TLR4−/− vs. WT to WT.
