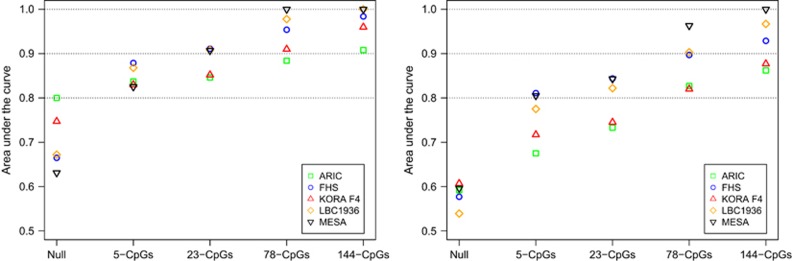
Figure 2.
A biomarker of heavy alcohol drinking. Four sets of cytosine-phosphate-guanine dinucleotides (CpGs) were selected at s=0.12 (5 CpGs), s=0.08 (23 CpGs), s=‘lambda.1se’ (78 CpGs) and s=‘lambda.min’ (144 CpGs) using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) in the Framingham Heart Study (FHS) cohort (the training cohort). ROC analysis was performed to classify heavy drinkers versus non-drinkers (left figure) and heavy drinkers versus light drinkers (right figure). ‘Non-drinkers’ were subjects with no alcohol consumption (i.e., g per day=0); ‘light drinkers’ were subjects who consumed 0<g per day⩽28 in men and 0<g per day⩽14 in women; ‘heavy drinkers’ were subjects who consumed ⩾42 g per day in men and ⩾28 g per day in women. ARIC, The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study; KORA F4, The Cooperative Health Research in the Region of Augsburg study; LBC1936, The Lothian Birth Cohort 1936; MESA, The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis.