Fig. 7.
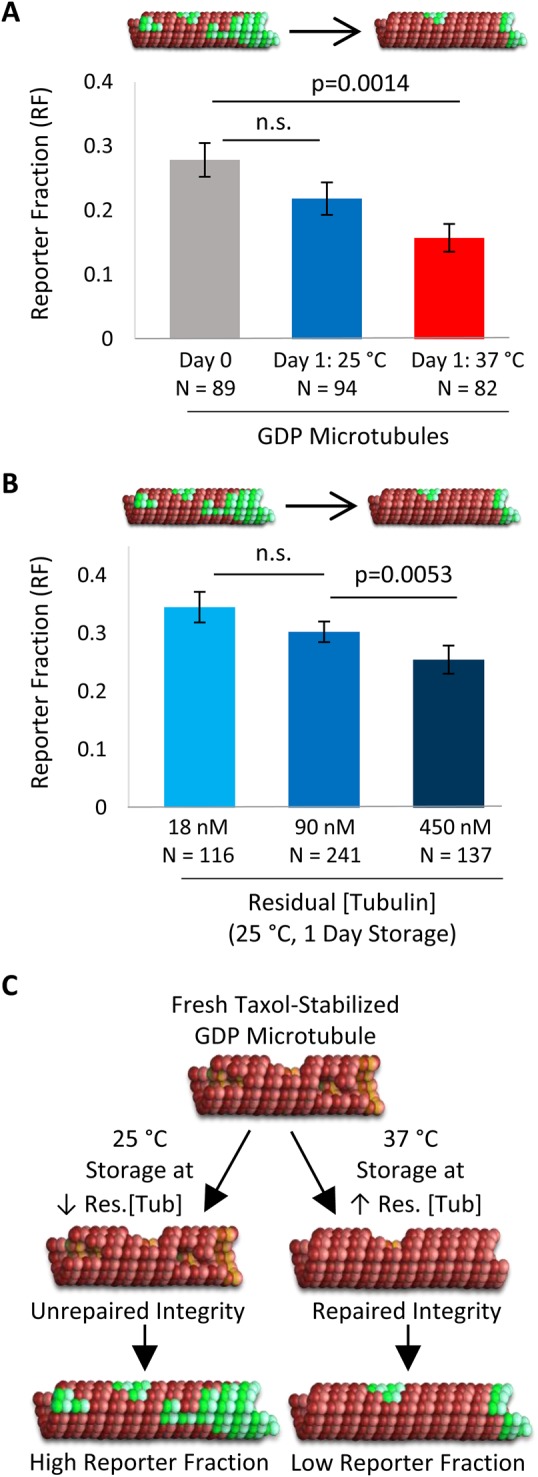
Impact of storage condition on microtubule lattice structural integrity. (A) Difference in Reporter Fraction after 1 day storage at 25°C or 37°C. (B) Altered residual free tubulin concentration during storage affects microtubule structure, as shown by Reporter Fraction: increased residual free tubulin leads to a decrease in Reporter Fraction, suggesting that Taxol-stabilized microtubules have fewer defects and gaps when they are stored under conditions of higher residual tubulin concentration. The bar graphs in A and B show the mean±s.e.m. repair fraction, weighted by microtubule length, and corrected for background contribution; P-values were calculated from Student's t-test. (C) Schematic demonstrating the proposed mechanism for changes in Taxol-stabilized GDP microtubules during storage: 25°C storage and low residual free tubulin concentration prevents repair of damaged microtubules (left, bottom). In contrast, 37°C storage and a higher residual free tubulin concentration lead to repair of damaged microtubules (right, bottom).
