Figure 6. Device evaluation using whole blood samples drawn from healthy donors and HIV-infected patients.
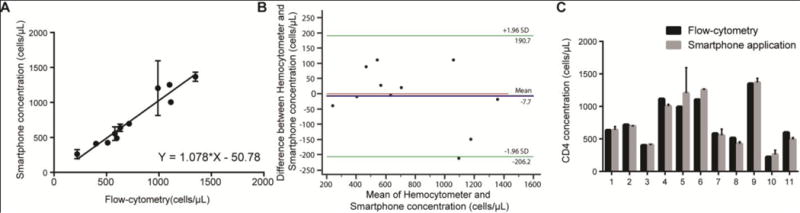
(A) Linear correlation between the results obtained by the smartphone-based system and FACS using whole blood (n=11). The pearson correlation coefficient was 0.97. (B) Bland-Altman analysis between the results obtained by FACs and the smartphone-based system. The blue line in this figure shows the mean difference of the methods, and the green lines represent the 95% limits of agreements (n=11). (C) Head-tohead comparison of concentration measurements made by both methods. Each value of x-axis represents a patient sample and t-tests revealed no statistical significance (P>0.05) between the two methods for all samples tested. Error bars in A and C represent the standard error of mean.
