Figure 3.
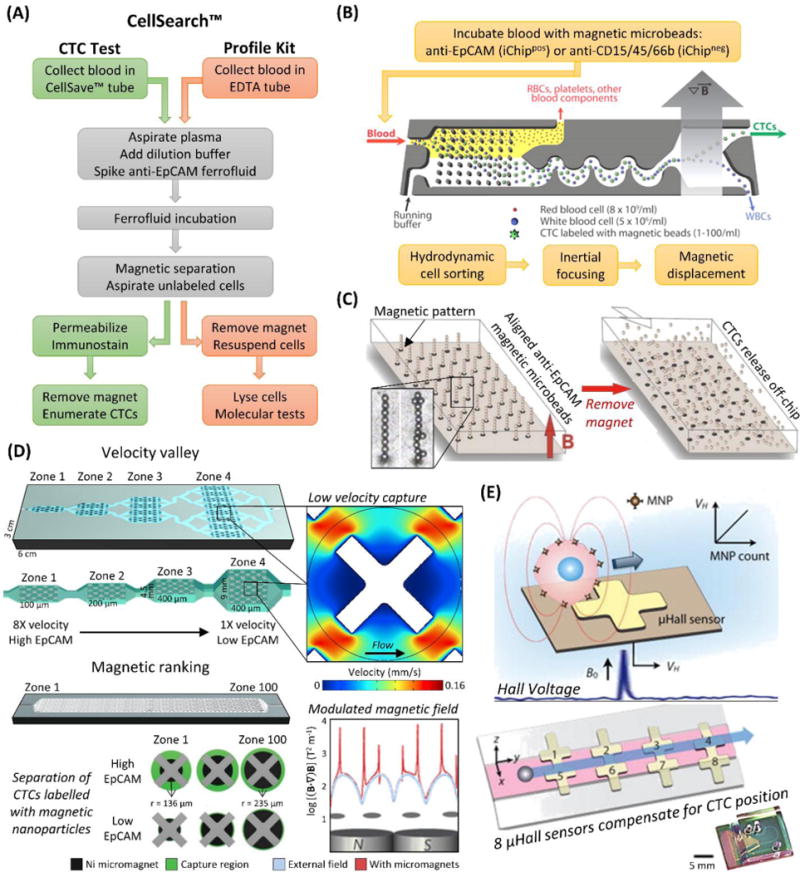
Magnetic CTC isolation technologies. (A) Workflow of the CellSearch™ CTC Test versus the CellSearch™ Profile Kit. (B) Workflow and diagram of the iChip, here shown in positive selection mode. The blood is debulked, the remaining cells are focused, and magnetically labelled cells (CTCs in positive selection mode, WBCs in negative selection) are preferentially forced into a separate outlet.107 (C) A diagram of the Ephesia microfluidic technology, which aligns anti-EpCAM magnetic microbeads into solid supports for CTC isolation that can be released by removing the magnetic field.33,60 (D) Velocity valley114,116 and magnetic ranking118 technologies for isolating magnetically labelled CTCs in zones of varying velocity or magnetic field strength, respectively, which provides phenotypic ranking of CTC antigen (e.g., EpCAM) expression in addition to enumeration. X-shaped microstructures reduce fluid velocity so magnetic forces can provide efficient CTC recovery. (E) The μHall device detects CTCs labelled with magnetic nanoparticles passing over a μHall sensor, which induces a voltage proportional to antigen expression. The sample stream (pink) is focused over 8 staggered μHall sensors that compensate for variable CTC position.121 Figure panels reproduced from reference107 with permission from The American Association for the Advancement of Science, copyright 2013; reference114 with permission from Wiley, copyright 2015; reference118 with permission from Nature Publishing Group, copyright 2017; and reference121 with permission from The American Association for the Advancement of Science, copyright 2012.
