Figure 5.
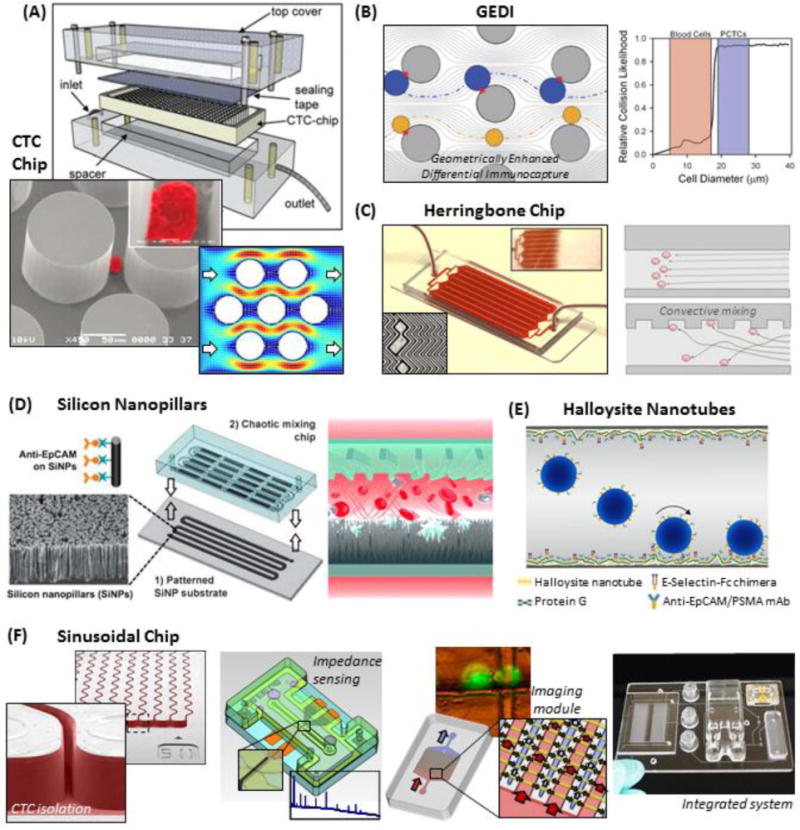
Positive-affinity microfluidic selection. (A) Assembly of the silicon CTC chip, SEM of a pseudo-coloured cell isolated on the Ab-coated micropillars, and simulated fluid velocity field in the device.36 (B) The GEDI device arranges micropillars to hydrodynamically induce a strong bias towards recovering cells >15–18 μm (blue) and minimizing smaller WBC (yellow) interactions.49 (C) The herringbone chip uses convective mixing to encourage CTCs to interact with Ab-coated surfaces.65 (D) A schematic of the silicon nanopillar chip, where a convective mixing chamber is attached to a nano-textured, Ab-coated Si substrate.128 (E) Polyurethane tubing is nano-textured with naturally occurring halloysite nanotubes and coated with Abs and selectins.262 (F) The thermoplastic-based sinusoidal chip uses narrow, Ab-coated microchannels to isolate CTCs.24 CTC release34,125 enables off-chip enumeration and viability testing by an impedance sensor and a microfluidic imaging module,74 which are integrated to a fluidic motherboard. Figure panels reproduced from reference36 with permission from Nature Publishing Group, copyright 2007; reference128 with permission from Wiley, copyright 2011; and reference74 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2013.
