Figure 7.
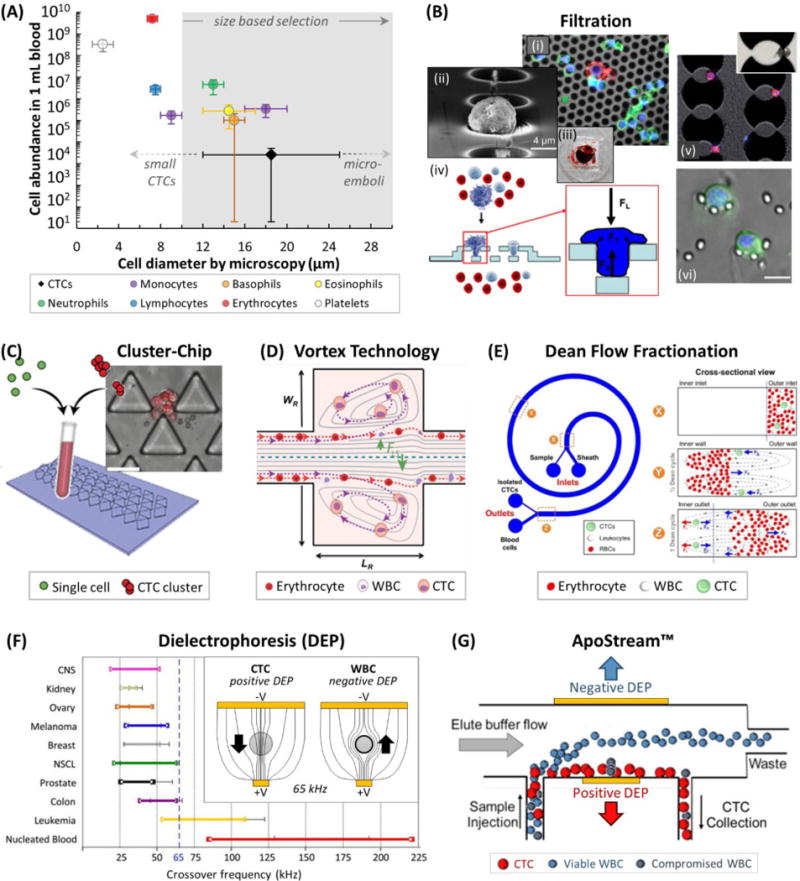
(A) Cell abundance versus cell diameter of blood cells27 and CTCs,78 and common size ranges for CTC discrimination.190,206 Note that WBC sizes can be smaller in free solution than when plated for microscopy.55,56 (B) (i) A CK(+)/DAPI(+) CTC (red and blue) amongst CD45(+)/DAPI(+) WBCs (green and blue) on a Si filter membrane.193 (ii) SEM of a fixed CTC on a 2D parylene-C membrane.195 (iii) Picture of a clogged filter after processing 7.5 mL of blood.192 (iv) Schematic of a 3D parylene-C membrane.190 (v) Brightfield and fluorescence images of MCF-7 cells filtered after size enlargement with anti-EpCAM microbeads.194 (vi) Images of CTCs trapped in a micropillar-based filtration device.198 (C) The Cluster-Chip collects CTC clusters specifically due to their size.50 (D) The Vortex Technology hydrodynamically traps large CTCs in side channels at high flow rates.56 (E) Dean Flow Fractionation is a hydrodynamic centrifugation method for size-dependent separation of CTCs.206 (F) Dielectrophoretic crossover frequencies for cancer cell lines, leukemia cell lines, and WBCs.263 (inset) Working principle of DEP showing field lines for positive and negative DEP experienced by CTCs and WBCs at 65 kHz, respectively.208 (G) Schematic of the ApoStream™ technology for DEP-flow field fractionation of CTCs.66 Figure panels reproduced from reference195 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2007; reference192 with permission from Nature Publishing Group, copyright 2014; reference190 with permission from Springer, copyright 2011; reference198 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2010; reference50 with permission from Nature Publishing Group, copyright 2015; reference206 with permission from Nature Publishing Group, copyright 2013; reference263 with permission from AIP Publishing, copyright 2013; and reference66 with permission from AIP Publishing, copyright 2012.
