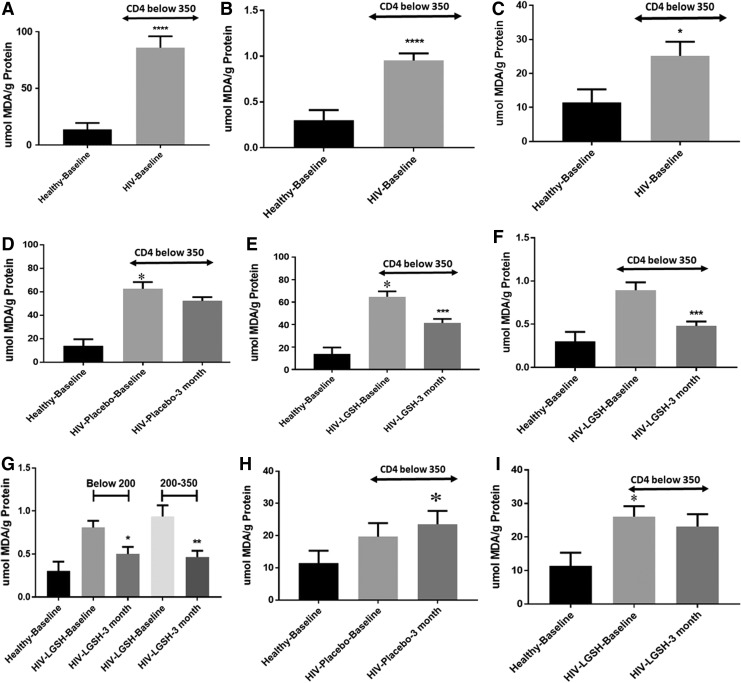
FIG. 2.
Measurement of MDA. (A) Baseline levels of MDA in plasma samples of Healthy Baseline and HIV-positive subjects with CD4 T cell counts below 350 cells/mm3. MDA levels in the plasma samples from HIV patients were significantly elevated compared to healthy individuals. MDA assay was performed using the TBARS assay kit from Cayman Chemical. Data represent mean ± SE from 16 healthy individuals and 30 individuals with HIV. (B) Baseline levels of MDA in RBCs of Healthy Baseline and HIV-positive subjects with CD4+ T cell counts below 350 cells/mm3. MDA levels in the RBCs from HIV patients were significantly enhanced compared to healthy individuals. Data represent mean ± SE from 16 healthy individuals and 30 individuals with HIV. (C) Baseline levels of MDA in CD4+ T cells of Healthy Baseline and HIV-positive subjects with CD4+ T cell counts below 350 cells/mm3. MDA levels in the CD4+ T cells from HIV patients were significantly higher compared to healthy individuals. Data represent mean ± SE from 16 healthy individuals and 30 individuals with HIV. (D) MDA levels in the plasma samples from the HIV placebo group with CD4+ T cell counts below 350 cells/mm3. There were no significant changes in the levels of MDA in the samples collected at 3 months postsupplementation with empty liposomes. Data represent mean ± SE from 16 healthy individuals and 15 individuals with HIV placebo. (E) MDA levels in the plasma samples from the HIV-L-GSH treatment group with CD4+ T cell counts below 350 cells/mm3. There was a significant decrease in the levels of MDA in the plasma samples from the HIV-positive subjects at 3 months post-L-GSH treatment. Data represent mean ± SE from 16 healthy individuals and 15 individuals with HIV-L-GSH. (F) MDA levels in the RBCs from the HIV-L-GSH treatment group with CD4+ T cell counts below 350 cells/mm3. There was a significant decrease in the levels of MDA in the RBCs from the HIV-positive subjects at 3 months post-L-GSH treatment. Data represent mean ± SE from 16 healthy individuals and 15 individuals with HIV-L-GSH. (G) MDA levels in RBCs from the HIV-L-GSH treatment group with CD4+ T cell counts below 200 cells/mm3 and between 200 and 350 cells/mm3. L-GSH treatment resulted in a significant reduction in the levels of MDA in the RBCs isolated from HIV-positive subjects with CD4 T cells below 200 cells/mm3 and in CD4 T cells between 200 and 350 cells/mm3 at 3 months postsupplementation. Data represent mean ± SE from 16 healthy individuals and seven individuals with HIV below 200 cells/mm3 and eight individuals with HIV 200–350 cells/mm3 with L-GSH supplementation. (H) MDA levels in the CD4+ T cells from the HIV placebo group with CD4+ T cell counts below 350 cells/mm3. There was a significant increase in the levels of MDA in the CD4+ T cells isolated from the HIV-positive subjects at 3 months post-treatment with empty liposomes. Data represent mean ± SE from 16 healthy individuals and 15 individuals with HIV placebo. (I) MDA levels in the CD4+ T cells from the HIV-L-GSH treatment group with CD4 T cell counts below 350 cells/mm3. There was stabilization in the levels of MDA in the CD4+ T cells isolated from the HIV-positive subjects at 3 months post-L-GSH treatment. Data represent mean ± SE from 16 healthy individuals and 15 individuals with HIV-L-GSH, *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.005; ****p ≤ 0.0005. MDA, malondialdehyde; RBC, red blood cell.